Before using this information and the product it supports, read the general information in Appendix C. Notices and the Warranty and Support Information on the Documentation CD.
Before installing this product, read the Safety Information.
Antes de instalar este produto, leia as Informações de Segurança.
Læs sikkerhedsforskrifterne, før du installerer dette produkt.
Lees voordat u dit product installeert eerst de veiligheidsvoorschriften.
Ennen kuin asennat tämän tuotteen, lue turvaohjeet kohdasta Safety Information.
Avant d'installer ce produit, lisez les consignes de sécurité.
Vor der Installation dieses Produkts die Sicherheitshinweise lesen.
Prima di installare questo prodotto, leggere le Informazioni sulla Sicurezza.
Les sikkerhetsinformasjonen (Safety Information) før du installerer
dette produktet.
Antes de instalar este produto, leia as Informações sobre Segurança.

Antes de instalar este producto, lea la información de seguridad.
Läs säkerhetsinformationen innan du installerar den här produkten.
This section contains information for trained service technicians.
Use the information in this section to help you identify potential unsafe conditions in an IBM product that you are working on. Each IBM product, as it was designed and manufactured, has required safety items to protect users and service technicians from injury. The information in this section addresses only those items. Use good judgment to identify potential unsafe conditions that might be caused by non-IBM alterations or attachment of non-IBM features or options that are not addressed in this section. If you identify an unsafe condition, you must determine how serious the hazard is and whether you must correct the problem before you work on the product.
Consider the following conditions and the safety hazards that they present:
To inspect the product for potential unsafe conditions, complete the following steps:
Observe the following guidelines when servicing electrical equipment:
All caution and danger statements in this documentation begin with a number. This number is used to cross reference an English caution or danger statement with translated versions of the caution or danger statement in the IBM Safety Information book.
For example, if a caution statement begins with a number 1, translations for that caution statement appear in the IBM Safety Information book under statement 1.
Be sure to read all caution and danger statements in this documentation before performing the instructions. Read any additional safety information that comes with the blade server or optional device before you install the device.
To avoid a shock hazard:
| To Connect: | To Disconnect: |
|---|---|
|
|

Do not:
Dispose of the battery as required by local ordinances or regulations.


Laser radiation when open. Do not stare into the beam, do not view directly with optical instruments, and avoid direct exposure to the beam.


 |
 |
 |
| >= 18 kg (39.7 lb) | >= 32 kg (70.5 lb) | >= 55 kg (121.2 lb) |
Hazardous voltage, current, and energy levels are present inside any component that has this label attached. There are no serviceable parts inside these components. If you suspect a problem with one of these parts, contact a service technician.
WARNING: Handling the cord on this product or cords associated with accessories sold with this product, will expose you to lead, a chemical known to the State of California to cause cancer, and birth defects or other reproductive harm. Wash hands after handling.
ADVERTENCIA: El contacto con el cable de este producto o con cables de accesorios que se venden junto con este producto, pueden exponerle al plomo, un elemento químico que en el estado de California de los Estados Unidos está considerado como un causante de cancer y de defectos congénitos, además de otros riesgos reproductivos. Lávese las manos después de usar el producto.
This Problem Determination and Service Guide contains information to help you solve problems that might occur when installing and using your IBM® BladeCenter®. It describes the diagnostic tools that come with the BladeCenter QS22, error codes and suggested actions. It also describes how to replace failing components.
Replaceable components are of three types:
For information about the terms of the warranty and getting service and assistance, see Warranty and Support Information.
In addition to this document, the following documentation also comes with the server:
This document is available in Portable Document Format (PDF) on the Documentation CD. It contains general information about the blade server, including how to install supported options and how to configure the blade server.
This document is on the Documentation CD. It contains translated caution and danger statements. Each caution and danger statement that appears in the documentation has a number that you can use to locate the corresponding statement in your language in the Safety Information document.
This document is in PDF on the Documentation CD. It contains information about the terms of the warranty and about service and assistance.
Depending on the server model, additional documentation might be included on the Documentation CD.
The blade server may have features that are not described in the documentation that comes with the server. The documentation might be updated occasionally to include information about those features, or technical updates might be available to provide additional information that is not included in the blade server documentation. The most recent versions of all BladeCenter documentation are at http://www.ibm.com/support/us/en/.
In addition to the documentation in this library, be sure to review the planning and installation documents for your BladeCenter hardware available at http://www.ibm.com/support/us/en/.
The IBM Software Development Kit for Multicore Acceleration documentation can be downloaded from http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/power/cell/. This contains information about how to install the operating system and how to program applications for the blade server.
Updates may be available for this and other BladeCenter documents. You can check for the most recent versions at http://www.ibm.com/support/us/en/ or on the BladeCenter Information center at http://publib.boulder.ibm.com/infocenter/systems/.
The caution and danger statements that appear in this document are also in the multilingual Safety Information document, which is on the Documentation CD. Each statement is numbered for reference to the corresponding statement in the Safety Information document.
The following notices and statements are used in this document:
The following table provides a summary of the features and specifications of the BladeCenter QS22.
Through the BladeCenter Advanced Management Module, you can view the blade server firmware code and other hardware configuration information.
The QS22 blade server is supported in the IBM BladeCenter H unit, the IBM BladeCenter HT unit, and the IBM BladeCenter S (non RAID type only) unit.
Providing it is supported by the BladeCenter unit, you can install and operate any other model of blade server in the same BladeCenter unit as a BladeCenter QS22.
The BladeCenter provides two options for storage:
SAS storage can be available through the following components: a SAS Expansion Card attached to the blade server, one or two SAS connectivity modules in the rear of the BladeCenter unit, and various options to attach the IBM BladeCenter Boot Disk System to the SAS connectivity modules. An optional SAS Expansion Card is available for the BladeCenter QS22.
If your QS22 blade server is installed in an IBM BladeCenter S unit, local SAS drives of the BladeCenter S unit, if present, are also available as storage.
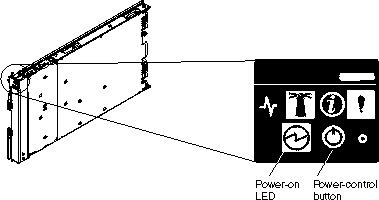
The QS22 blade server is hot-swappable and can be inserted into the BladeCenter unit when the unit is already powered up. However, it can only be powered on by one of the methods described in this section. While the blade server is powering up, the power-on LED on the front of the server is lit. See Blade server controls and LEDs for the power-on LED states.
After you have installed the blade server into a powered up BladeCenter unit, wait until the power on LED on the blade server flashes slowly before turning on the blade server.
You can turn on the blade server in any of the following ways:
In the event of a power failure the BladeCenter unit and then the blade server can start automatically when power is restored. You must configure this through the BladeCenter Advanced Management Module. See the BladeCenter Management Module User's Guide for further information about this feature.
When you turn off the blade server, it is still connected to power through the BladeCenter unit and can continue to respond to requests from the service processor, including remote requests to turn the blade server on. To remove all power from the blade server, you must physically remove it from the BladeCenter unit or power off the BladeCenter unit.
To avoid loss of data, shut down the Linux® operating system before you turn off the blade server. Shut down the operating system by entering the shutdown -h now command at the command prompt or by choosing shutdown if you are using a graphical user interface (GUI). See your operating system documentation for additional information about shutting down the operating system.
If the BladeCenter unit has not been turned off, the blade server can be turned off in any of the following ways:
This section describes the controls and LEDs on the front panel of the blade server. For further information about the LEDs and how they can be used to assist in troubleshooting, see Problems indicated by the front panel LEDs.
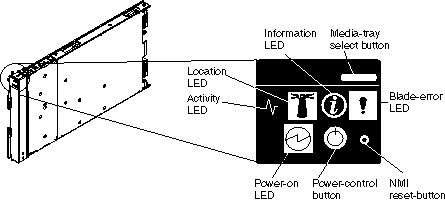
It can take approximately 20 seconds for the operating system on the blade server to recognize the media tray.
The blade error LED, information LED, and location LED can be turned off through the Advanced Management Module Web interface.
The QS22 blade server has status LEDs on the system board to indicate the health of various components. Some are within the light box while others are in different locations. A lit LEDs indicates an error condition. Complete information about the LEDs can be found in Troubleshooting charts.
To find out what if any errors have occurred on the system board, you must:
This lights any error LEDs that were turned on during processing. It also lights a green LED to indicate the capacitor is charged and the light path diagnostics system is operating.
Figure 3 shows the location of the light path LEDs and the diagnostics switch.
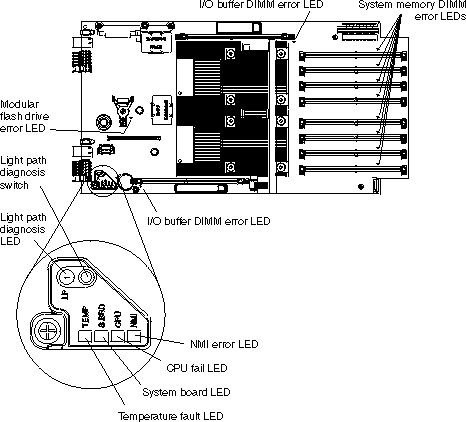
Pressing the light path diagnostics switch lights the appropriate LED to indicate where an error has occurred.
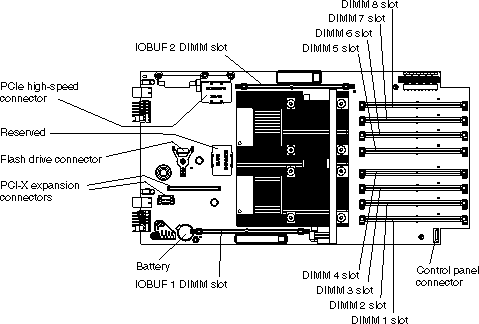
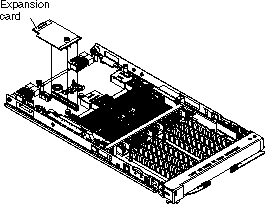
The following illustration shows the location of the connectors for user-installable options.
This chapter describes how to:
You do not have to boot the operating system before you can communicate with the QS22 blade server. You can access it through:
The Advanced Management Module is the main means of administering the BladeCenter system. Use the Advanced Management Module Web-based management and configuration program to:
Complete the following steps to start the Web-based management and configuration program:
192.168.70.125
The Enter Network Password window opens.
The initial user ID and password for the Advanced Management Module are:
The BladeCenter management and configuration window opens.
For additional information, see the IBM BladeCenter Advanced Management Module User's Guide.
The IBM BladeCenter Advanced Management Module also provides a command-line interface to provide direct access to BladeCenter management functions. You can use this as an alternative to using the BladeCenter Management Module Web interface.
Through the command-line interface, you can issue commands to control the power and configuration of the blade server and other components in the BladeCenter unit. For information and instructions, see the IBM BladeCenter Management Module Command-Line Interface Reference Guide.
To establish a Serial over LAN (SOL) connection to the blade server, you must configure the SOL feature for the blade server and start an SOL session as described in the IBM BladeCenter Serial over LAN Setup Guide. In addition, the Advanced Management Module must be configured as described in the IBM BladeCenter Management Module User's Guide, and the BladeCenter unit must be configured as described in the IBM BladeCenter Serial over LAN Setup Guide.
Use the serial interface to:
You can connect a PC serially through the BladeCenter unit using a specific UART cable. To connect to the serial console, plug the serial cable into the BladeCenter unit and connect the other end to a serial device or computer with a serial port. For more information, see the Installation and User's Guide for your BladeCenter unit.
Set the following parameters for the serial connection on the terminal client:
By default, the blade server sends output over SOL and to the serial port on the BladeCenter unit. However, the default for input is to use SOL. If you wish to use a device connected to the serial port for input you must press any key on that device while the blade server boots.
The Advanced Management Module is the main means of administering the BladeCenter unit and the blade servers. However, another utility is provided which in some cases can give more information than that displayed in the Advanced Management Module. This is the System Management Services (SMS) utility program.
The SMS utility program allows you to view and update the VPD, change the boot list and set network parameters.
Complete the following steps to start SMS:
For example, to power cycle and start an SOL remote text console with a blade server that is in the first bay of the BladeCenter unit, issue the command:
power -cycle -c -T system:blade[1]
To open a console session with a blade that is already powered on, use the command:
console -T system:blade[1]
QS22 Firmware Starting Check ROM = OK Build Date = Jan 4 2008 11:31:29 FW Version = "QD-1.26.0-0" Press "F1" to enter Boot Configuration (SMS) Press "F2" to boot once from CD/DVD
Press F1 to display the SMS menu.
The VPD on each blade server contains details about the machine type or model, serial number and the universal unique ID.
Complete the following steps to see this information:
PowerPC Firmware
Version QD0123000
SLOF-SMS 1.1 (c) Copyright IBM Corp. 2007 All rights reserved.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Main Menu
1. Select Language
2. Setup Remote IPL (Initial Program Load)
3. Change SCSI Settings
4. Select Console
5. Select Boot Options
6. Firmware Boot Side Options
7. Progress Indicator History
8. FRU Information
9. Change SAS Boot Device
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Navigation Keys:
X = eXit System Management Services
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Type menu item number and press Enter or select Navigation key:
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
PowerPC Firmware Version QD0123000 SLOF-SMS 1.1 (c) Copyright IBM Corp. 2007 All rights reserved. -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- FRU Information Machine Type and Model: 079338x Machine Serial Number: ABCDEFG Universal Unique ID: 12345678-1234-1234-1234-123456789ABC -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Navigation Keys: M = return to Main Menu ESC key = return to previous screen X = eXit System Management Services -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select Navigation key :
When you replace a FRU details are not recorded in the VPD. You must enter them manually through SMS.
When the system firmware detects an FRU replacement part during boot the process stops to allow you to enter the machine type or model and serial number. Boot does not continue until the information is provided.
To enter new FRU information, complete the following steps:
PowerPC Firmware
Version QD0123000
SLOF-SMS 1.1 (c) Copyright IBM Corp. 2007 All rights reserved.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Enter Type Model Number
(Must be 7 characters, only A-Z, a-z, 0-9 allowed. Press Esc to skip)
Enter Type Model Number :
Type the model number according to the instructions on the screen and press Enter to continue.
PowerPC Firmware
Version QD0123000
SLOF-SMS 1.1 (c) Copyright IBM Corp. 2007 All rights reserved.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Number entered is: 1234567
Accept number?
(Enter 'y' or 'Y' to accept or 'n' or 'N' to decline)
Select Navigation key : Type y or Y and press Enter to confirm
the number.PowerPC Firmware
Version QD0123000
SLOF-SMS 1.1 (c) Copyright IBM Corp. 2007 All rights reserved.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Enter Serial Number
(Must be 7 characters, only A-Z, a-z, 0-9 allowed)
Enter Serial Number :
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------Press Enter to continue.PowerPC Firmware
Version QD0123000
SLOF-SMS 1.1 (c) Copyright IBM Corp. 2007 All rights reserved.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Number entered is: ABCDEFG
Accept number?
(Enter 'y' or 'Y' to accept or 'n' or 'N' to decline)
Select Navigation key :
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------Type y or Y and press Enter to
confirm the number.
This completes the process and the blade server continues to boot as normal.
The firmware consists of two distinct packages:
The packages are delivered separately and do not follow the same versioning scheme.
IBM periodically makes updates to both BMC and system firmware. These may be downloaded from http://www.ibm.com/support/us/en/.
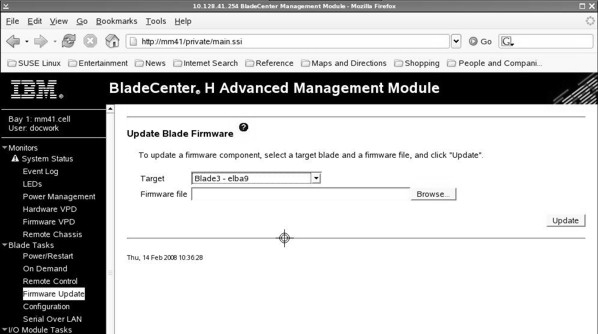
Complete the following steps to update the BMC and system firmware images:
Complete the following steps to view the current firmware code levels for both the BMC and the system firmware:
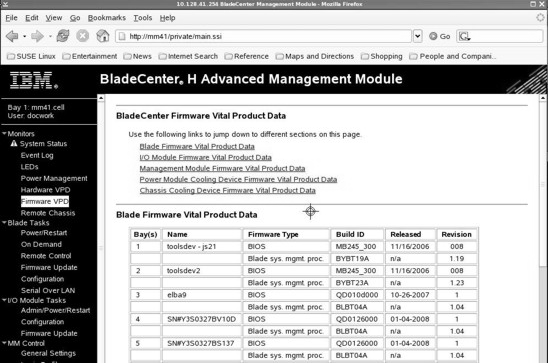
Compare this information to the firmware information provided at http://www.ibm.com/support/us/en/. If the two match, then the blade server has the latest firmware. If not, download the firmware package from the IBM Support Web site. See Updating the BMC firmware or the IBM Support Web site for installation instructions.
You can also view the system firmware level from within the operating system by using the following command:
xxd /proc/device-tree/openprom/ibm,fw-vernum_encoded
Output is similar to:
0000000: 5142 3031 3031 3030 3000 00 QB0101000..
where QB0101000 is the system firmware version.
You can update the BMC firmware from the Linux prompt using the update package or from the Advanced Management Module.
Complete the following steps to update the BMC firmware from the Linux command prompt:
Complete the following steps to update the BMC firmware:
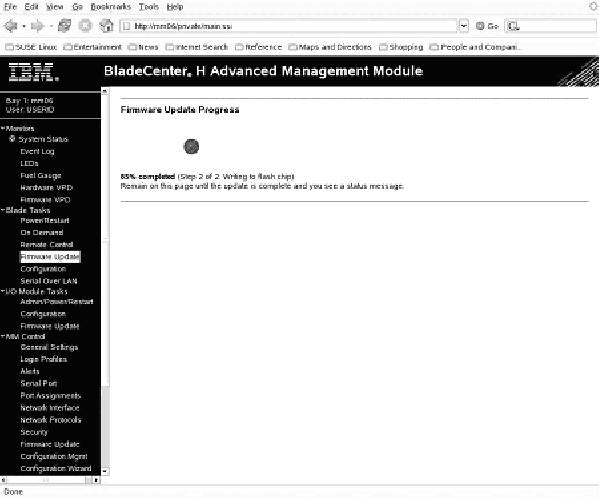
System firmware can only be installed after the operating system has booted. If the operating system is not installed or cannot boot, then no upgrade or recovery is possible. See the other sections of the manual Diagnostics and troubleshooting for further information about troubleshooting the QS22 blade server.
You can update the system firmware:
For all the above options Linux needs to have a current version of rtas_flash device driver installed. This is normally installed with the operating system. If it is not, see the installation guide for the Software Development Kit for Multicore Acceleration for instructions about how to get this device driver and install it.
You can now update firmware using the update packages available from http://www.ibm.com/support/us/en/. These can be installed either through IBM Director or by executing the .sh file contained in the package. This section describes how to use the update package to install the firmware update or extract the firmware image for manual installation.
To install the firmware package using IBM Director, see the documentation on the IBM Director CD.
The update package consists of 4 files:
The package consists of an file with a .sh extension that runs from the Linux prompt. It has a number of options. To see what options are available, run the package without any options or with the -h switch:
# ./ibm_fw_bios_qb-1.9.1-2_linux-pq_cell.sh
In this example, ibm_fw_bios_qb-1.9.1-3_linux-pq_cell.sh is the name of the firmware update package. The file name changes according to the version of the firmware.
A screen similar to the following appears:
Usage: -x /someDirectory - Extract the payload to <some directory> -xr /someDirectory - Extract the payload plus PkgSdk files to <some directory> -xd /dev/fd0 - Create a DOS bootable diskette - Internel floppy drive -xd /dev/sda - Create a DOS bootable diskette - External USB floppy drive -u - Perform update unattended -h - Display this help screen ++debug - Display helpful debug information Note: All other command line arguments are passed to the payload executable
The -xd options are not supported on the QS22 blade server.
Complete the following steps to update the firmware automatically using the update package:
./ibm_fw_bios_qb-1.9.1-2_linux-pq_cell.sh -u
If you cannot update the firmware using the update_flash script, it is possible to update the firmware manually. You can use rtas_flash over /proc.
Complete the following steps to install the firmware manually:
./<update package> -x <target directory>For example, to extract the image package ibm_fw_bios_qb-1.9.1-2.sh from ibm_fw_bios_qb-1.9.1-2_linux-pq_cell.sh in the directory /temp/fwimage enter:
./ibm_fw_bios_qb-1.9.1-2_linux-pq_cell.sh -x /temp/fwimageIf the directory does not exist the firmware package creates it.
./<image package> -xFor example, to extract the image file QB-1.9.1-2-boot_rom.bin from ibm_fw_bios_qb-1.9.1-2.sh enter:
./ibm_fw_bios_qb-1.9.1-2.sh -x
modprobe rtas_flash
cp <image-file> /proc/ppc64/rtas/firmware_update shutdown --r now
For example, to copy the image file cp QB-1.9.1-2-boot_rom.bin to /proc/ppc64/rtas/firmware_update enter:
cp QB-1.9.1-2-boot_rom.bin /proc/ppc64/rtas/firmware_update shutdown --r now
Once the system firmware is updated, the QS22 blade server boots from the new firmware. However, there are always two copies of the system firmware image on the blade server:
Once you have updated the system firmware and booted the blade server, you should copy the TEMP image to the PERM image. This ensures that the PERM and TEMP images are at the same revision level. The TEMP and PERM images should always be at the same revision level.
There are two commands you can use to update an old image on PERM.
update_flash -c
echo 0 > /proc/rtas/manage_flash
For more information on booting from the TEMP or PERM images, see Recovering the system firmware code.
If you have installed the SAS optional expansion card or a high-speed expansion card, for example the InfiniBand card, you may have to update the firmware. See the documentation that comes with the components for instructions about how to update the firmware.
IBM periodically makes updates available for both SAS and high-speed expansion cards. These may be downloaded from http://www.ibm.com/support/us/en/.
One dual-port Gigabit Ethernet controller is integrated on the blade server system board. Each controller port provides a 1000-Mbps full-duplex interface connecting to one of the Ethernet Switch Modules in I/O bays 1 and 2 of the BladeCenter unit, which enables simultaneous transmission and reception of data on the Ethernet local area network (LAN).
Each Ethernet-controller port on the system board is routed to a different switch module in I/O bay 1 or bay 2. The routing from the Ethernet-controller port to the I/O bay varies according to whether an Ethernet adapter is enabled and the operating system that is installed. See Blade server Ethernet controller enumeration for information about how to determine the routing from the Ethernet-controller ports to I/O bays for your blade server.
You do not have to set any jumpers or configure the controller for the blade server operating system. However, you must install a device driver to enable the blade server operating system to address the Ethernet-controller ports. For device drivers and information about configuring your Ethernet controller ports, see the Ethernet software documentation that comes with your blade server, or contact your IBM marketing representative or authorized reseller. For updated information about configuring the controllers, go to the Barcelona Computing Centre Web site at http://www.bsc.es/projects/deepcomputing/linuxoncell/.
To update the Ethernet controller firmware, you must download an update package from http://www.ibm.com/support/us/en/. This section describes how to use the update package to install the firmware update.
The update package consists of four files:
The package consists of an file with a .sh extension that runs from the Linux prompt. It has a number of options. To see what options are available, run the package without any options or with the -h switch:
# ./brcm_fw_nic_2.0.3-e-1_rhel5_cell.sh
In the example shown above, brcm_fw_nic_2.0.3-e-1_rhel5_cell.sh is the name of the firmware update package. The file name changes according to the version of the firmware.
A screen similar to the following appears:
Usage: -x /someDirectory - Extract the payload to <some directory> -xr /someDirectory - Extract the payload plus PkgSdk files to <some directory> -xd /dev/fd0 - Create a DOS bootable diskette - Internel floppy drive -xd /dev/sda - Create a DOS bootable diskette - External USB floppy drive -u - Perform update unattended -h - Display this help screen ++debug - Display helpful debug information
The -xd and -x options are not supported on QS22.
The -u option performs an unattended and automatic update of the firmware. The blade server reboots automatically as part of the update process.
Complete the following steps to update the firmware automatically:
./ brcm_fw_nic_2.0.3-e-1_rhel5_cell.sh -u
During the update process, messages similar to the following appear on the console:
[root@c4b14 brcm-2.0.3-ppc]# ./ brcm_fw_nic_2.0.3-e-1_rhel5_cell.sh -u
IBM Ethernet Firmware Update Tool, Version 1.0.2
Warning. No Broadcom NetXtreme II adapters found.
ADAPTER MAC BOOT IPMI ASF PXE UMP
------------------- ---- ---- --- --- ---
001A640E030C (5704s) 3.21 2.20 NA NA NA
001A640E030D (5704s) NA NA NA NA NA
Updating Broadcom NetXtreme adapters.
Updating 001A640E030C using file 16A8bc.bin ---> Update successful
Updating 001A640E030C using file 16A8ipmi.bin ---> Update successful
Error! Firmware not detected on device 001A640E030D.
Warning. No Broadcom NetXtreme II adapters found.
ADAPTER MAC BOOT IPMI ASF PXE UMP
------------------- ---- ---- --- --- ---
001A640E030C (5704s) 3.38 2.47 NA NA NA
001A640E030D (5704s) NA NA NA NA NA
One or more errors occurred during the firmware update process. See /var
The enumeration of the Ethernet controller or controller ports in a blade server is operating system dependent. You can verify the Ethernet controller or controller port designations that a blade server uses through your operating system settings.
The routing of an Ethernet controller or controller port to a particular BladeCenter unit I/O bay depends on the type of Ethernet controller that is installed. You can verify which Ethernet-controller port is routed to which I/O bay by using the following test:
Communications from optional I/O expansion cards are routed to I/O bays 3 and 4. If you have installed an I/O expansion card on the blade server you can verify which controller port on an expansion card is routed to which I/O bay by performing the same test, using a controller on the expansion card and a compatible switch module or pass-thru module in I/O bay 3 or 4.
This parts listing supports BladeCenter QS22 replaceable components. To check for an updated parts list on the Web, do the following:
Replaceable components are of three types:
For information about the terms of the warranty and getting service and assistance, see Warranty and Support Information.
The following table lists which replaceable components are available for the BladeCenter QS22.
| Description | FRU No. | Tier 1 CRU No. | Tier 2 CRU No. |
|---|---|---|---|
| DIMM VLP 1 GB DDR2 system memory | 46C0502 | ||
| DIMM VLP 2 GB DDR2 system memory | 46C0515 | ||
| DIMM VLP 4 GB DDR2 system memory | 46C0516 | ||
| DIMM VLP 1 GB DDR2 I/O buffer memory only | 46C0502 | ||
| Cisco 4X Infiniband Expansion Card for IBM BladeCenter | 32R1763 | ||
| Front bezel assembly | 43W9932 | ||
| BladeCenter QS22 blade assembly, base and planar | 60H3199 | ||
| SAS expansion card | 39Y9188 | ||
| BladeCenter PCI Express I/O Expansion Unit | 43W4390 | ||
| Air baffle for I/O buffer DIMM connector | 60H2962 | ||
| Mounting tray for modular flash drive | 42C0593 | ||
| 8 GB Modular Flash Drive | 43W3932 | ||
| 8 GB IBM Modular Solid State Disk | 60H4322 | ||
| Miscellaneous Parts Kit | 60H3473 | ||
| Blade Cover and Warning Label | 46C7201 | ||
| System Service Label | 60H3471 | ||
| FRU List Label | 60H3472 |
Part numbers can change and other options can become available. For the latest information, check the IBM Web site at http://www.ibm.com/support/us/en/.
Consumable parts are not covered by the IBM Statement of Limited Warranty. The following consumable parts are available for purchase from the retail store:
| Description | Part Number |
|---|---|
| 3V lithium battery | 43W9859 |
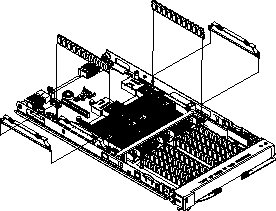
This chapter provides instructions for installing or replacing units on the blade server. Replaceable units are components, such as memory modules, and I/O expansion cards. Some removal instructions are provided in case you need to replace one replaceable unit with another.
You can replace the following items:
Before you begin, read the following:
To help ensure proper cooling and system reliability, be sure that:
To reduce the possibility of electrostatic discharge, observe the following precautions:
The blade server is a hot-swappable device, and the blade bays in the BladeCenter unit are hot-swappable bays. Therefore, you can install or remove the blade server without removing power from the BladeCenter unit. However, you must turn off the blade server before removing it from the BladeCenter unit.
If you reinstall the blade server into a different bay, you might have to reconfigure the blade server.
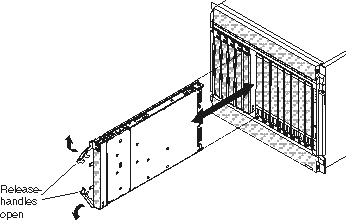
Complete the following steps to remove the blade server:
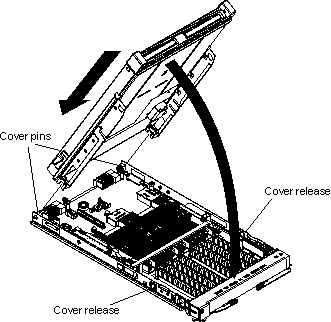
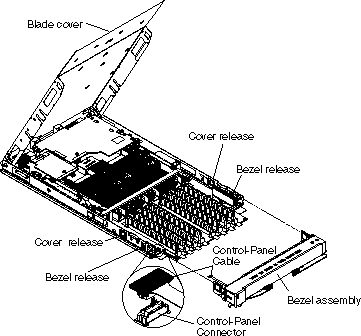
You must open the blade server cover to access, install or remove any of the replaceable items.
If a BladeCenter PCI Express I/O Expansion Unit has been installed on your blade server, ignore this section and follow the instructions in Removing the BladeCenter PCI Express I/O Expansion Unit instead.
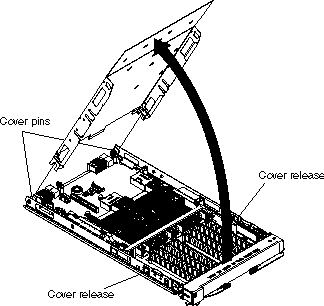
Complete the following steps to open the blade server cover:
You must remove BladeCenter PCI Express I/O Expansion Unit, if installed, to access, install or remove any of the replaceable items.
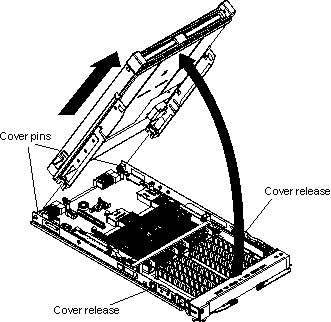
Complete the following steps to remove BladeCenter PCI Express I/O Expansion Unit:
Before you can add, remove, or replace system memory DIMM modules, replace a defective system board assembly, or replace the blade server front bezel assembly, you must first remove the blade server front bezel assembly.
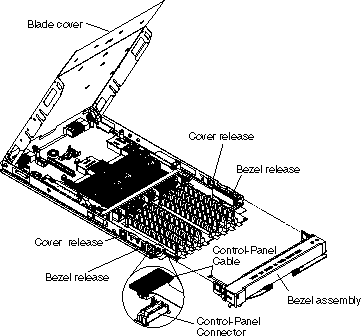
Complete the following steps to remove the front bezel assembly:
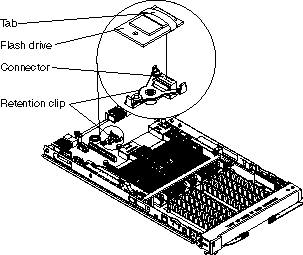
The modular flash drive connects to the flash drive connector on the system board and provides non-volatile memory. This may be used, for example, for installing an operating system.
Complete the following steps to install the modular flash drive:
If you have other options to install or remove, do so now. Otherwise, go to Finishing the installation.
Complete the following steps to remove the modular flash drive:

If the modular flash drive is blocked by a high-speed expansion card, you must remove the high-speed expansion card before removing the modular flash drive. See Removing an optional high-speed expansion card.
If you have other options to install or remove, do so now. Otherwise, go to Finishing the installation.
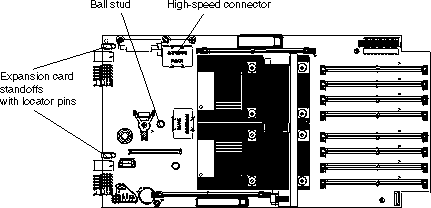
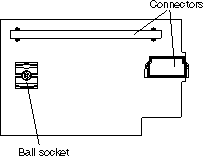
You can connect a high-speed expansion card, for example an InfiniBand card, to the high-speed connector on the system board. Use the two expansion card locator pins to assist with fitting the card. If your card has a ball socket, use the socket to lock the card in place.
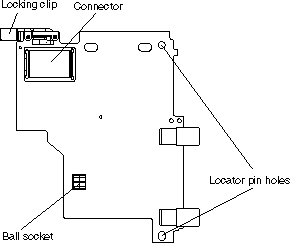
Complete the following steps to install the high-speed expansion card:
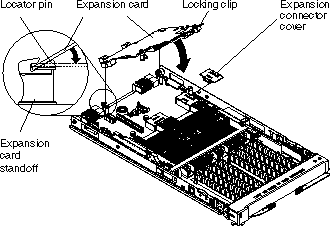
If you have other options to install or remove, do so now. Otherwise, go to Finishing the installation.
If you wish to remove an optional high-speed expansion card, complete the following steps.
For diagrams see Installing an optional high-speed expansion card.
There are 8 DIMM slots for system memory. Each IBM PowerXCell 8i processor has two memory channels and there are two DIMM slots per memory channel.
You can use VLP DDR2 1 GB, 2 GB, or 4 GB memory modules. The maximum memory configuration has a 4 GB memory module in each DIMM slot which provides 16 GB to each processor and 32 GB in total.
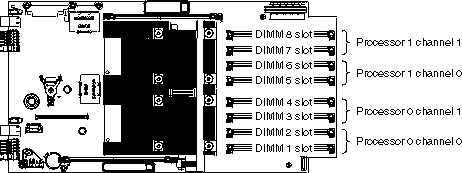
As shown in Figure 14, each processor has a channel 0 and a channel 1, with a pair of DIMM slots for each channel. To use a channel, you must populate both DIMM slots that belong to the channel.
All DIMM configuration listed in Table 2 are supported by the latest firmware level.
| IBM PowerXCell 8i-0 | IBM PowerXCell 8i-1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Channel 0 | Channel 1 | Channel 0 | Channel 1 | ||||
| Slot 1 | Slot 2 | Slot 3 | Slot 4 | Slot 5 | Slot 6 | Slot 7 | Slot 8 |
| 1 GB | 1 GB | 1 GB | 1 GB | ||||
| 1 GB | 1 GB | 2 GB | 2 GB | ||||
| 1 GB | 1 GB | 4 GB | 4 GB | ||||
| 2 GB | 2 GB | 1 GB | 1 GB | ||||
| 2 GB | 2 GB | 2 GB | 2 GB | ||||
| 2 GB | 2 GB | 4 GB | 4 GB | ||||
| 4 GB | 4 GB | 1 GB | 1 GB | ||||
| 4 GB | 4 GB | 2 GB | 2 GB | ||||
| 4 GB | 4 GB | 4 GB | 4 GB | ||||
| 1 GB | 1 GB | 1 GB | 1 GB | 1 GB | 1 GB | 1 GB | 1 GB |
| 1 GB | 1 GB | 1 GB | 1 GB | 2 GB | 2 GB | 2 GB | 2 GB |
| 1 GB | 1 GB | 1 GB | 1 GB | 4 GB | 4 GB | 4 GB | 4 GB |
| 2 GB | 2 GB | 2 GB | 2 GB | 1 GB | 1 GB | 1 GB | 1 GB |
| 2 GB | 2 GB | 2 GB | 2 GB | 2 GB | 2 GB | 2 GB | 2 GB |
| 2 GB | 2 GB | 2 GB | 2 GB | 4 GB | 4 GB | 4 GB | 4 GB |
| 4 GB | 4 GB | 4 GB | 4 GB | 1 GB | 1 GB | 1 GB | 1 GB |
| 4 GB | 4 GB | 4 GB | 4 GB | 2 GB | 2 GB | 2 GB | 2 GB |
| 4 GB | 4 GB | 4 GB | 4 GB | 4 GB | 4 GB | 4 GB | 4 GB |
To change the system memory configuration, complete the following steps:
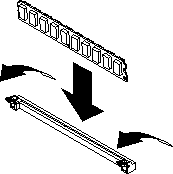
If you have other options to install or remove, do so now. Otherwise, go to Finishing the installation.
This section describes how to add I/O buffer memory. For instructions on how to add system memory see Adding or changing system memory.
Each IBM PowerXCell 8i companion chip has one DIMM slot for I/O buffer memory. The QS22 blade server supports VLP DDR2 1 GB DIMMs. You must add memory as a pair of DIMMs, one for each IBM PowerXCell 8i companion chip.
To install I/O buffer memory, complete the following steps:
There are two DIMM slots, one for each IBM PowerXCell 8i companion chip. The slots are labelled IOBUF 1 and IOBUF 2. You must install a 1 GB DIMM for both IBM PowerXCell 8i companion chips.
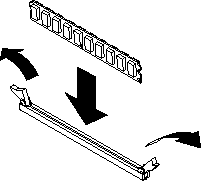
If you have other options to install or remove, do so now. Otherwise, go to Finishing the installation.
For the QS22 cooling system to work properly there must be no empty I/O buffer DIMM slots. The unused slots must be fitted with DIMM fillers. Replace faulty DIMM fillers and, if you remove the I/O buffer memory modules, fit empty slots with DIMM fillers.
To install or replace DIMM fillers, complete the following steps:
If you have other options to install or remove, do so now. Otherwise, go to Finishing the installation.
The QS22 blade server does not have any built-in disk storage. The SAS expansion card allows you to use SAS attached storage. Use the blue handling areas to handle the card.
Complete the following steps to install the SAS expansion card:
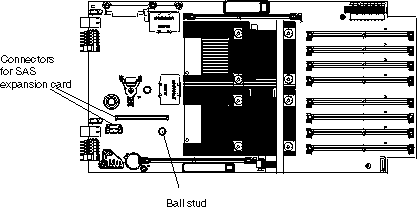
If you have other options to install or remove, do so now. Otherwise, go to Finishing the installation.
Complete the following steps to install the BladeCenter PCI Express I/O Expansion Unit:
The system board is a field replaceable unit (FRU): FRUs must be installed only by trained service technicians.
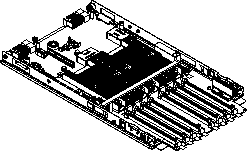
Complete the following steps to replace the system board base and planar:
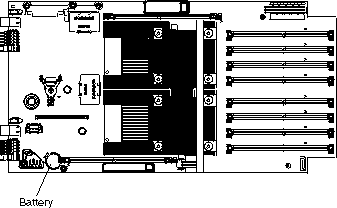
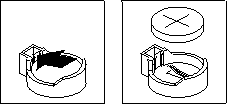
IBM has designed this product with your safety in mind. The lithium battery must be handled correctly to avoid possible danger. If you replace the battery, you must adhere to the following instructions.
If you replace the original lithium battery with a heavy-metal battery or a battery with heavy-metal components, be aware of the following environmental consideration. Batteries and accumulators that contain heavy metals must not be disposed of with normal domestic waste. They will be taken back free of charge by the manufacturer, distributor, or representative, to be recycled or disposed of in a proper manner.
To order replacement batteries, call 1-800-IBM-SERV within the United States, and 1-800-465-7999 or 1-800-465-6666 within Canada. Outside the U.S. and Canada, call your IBM authorized reseller or IBM marketing representative.

Do not:
Dispose of the battery as required by local ordinances or regulations.
Complete the following steps to replace the battery:
The retention clip supports the modular flash drive and should be replaced if damaged.
To remove and replace the retention clip, complete the following steps:

The miscellaneous parts kit contains replacement parts and screws to be used if the original item is damaged. It contains the following items:
To replace a support or bracket you need a Philips head screwdriver.
The ball studs help support the optional expansion cards and should be replaced if damaged.
To remove and replace a ball stud, complete the following steps:

To complete the installation you must:
Figure 24 shows how to install the front bezel assembly on the blade server.
Complete the following steps to install the blade server front bezel assembly:
Important: The blade server cannot be inserted into the BladeCenter unit until the cover is installed and closed or an expansion unit is installed. Do not attempt to override this protection.
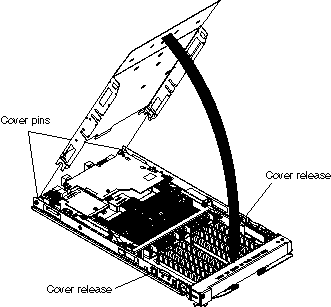
Complete the following steps to close the blade server cover:
The BladeCenter unit contains the input/output connectors that are available to the blade server. See the documentation that comes with the BladeCenter unit for information about the input/output connectors.
This chapter provides basic troubleshooting information to help you solve some common problems that might occur while setting up your blade server.
A problem with the BladeCenter QS22 can relate either to the BladeCenter QS22 or the BladeCenter unit.
A problem with the blade server exists if the BladeCenter unit contains more than one blade server and only one of the blade servers has the symptom. If all of the blade servers have the same symptom, then the problem relates to the BladeCenter unit. For more information, see the Problem Determination and Service Guide for your BladeCenter unit.
The BladeCenter QS22 blade server is supported in the IBM BladeCenter H unit, the IBM BladeCenter HT unit, and the IBM BladeCenter S (non RAID type only) unit.
You can put other blade server types that are supported in your BladeCenter unit in the same unit as a BladeCenter QS22.
Before you start problem determination or servicing, check that:
If you install the blade server in the BladeCenter unit and the blade server does not start, always perform the following basic checks before continuing with more advanced troubleshooting:
Table 3 describes where to find troubleshooting information in this section.
| Component | Where to find information |
|---|---|
|
SAS expansion card
Front bezel
High-speed InfiniBand expansion card
Modular flash drive |
Solving undetermined problems |
| Memory | Table 12 |
|
LEDs
Power
Network connections
Service processor
Software problems |
Troubleshooting charts |
For troubleshooting information about other BladeCenter components, see the appropriate Problem Determination and Service Guide, and other product-specific documentation. See Related documentation for additional information. For the latest editions of the IBM BladeCenter documentation, go to http://www.ibm.com/support/us/en/ on the World Wide Web.
The following tables list problem symptoms and suggested solutions. If you cannot find the problem in the troubleshooting charts, or if carrying out the suggested steps do not solve the problem, have the blade server serviced.
If you have problems with an adapter, monitor, keyboard, mouse, or power module, see the Problem Determination and Service Guide for your BladeCenter unit for more information.
If you have problems with an Ethernet switch module, I/O adapter, or other optional device that can be installed in the BladeCenter unit, see the Problem Determination and Service Guide or other documentation that comes with the device for more information.
The state of the LEDs on the front of the blade can help in isolating problems.

The table below gives an explanation and a suggested action, if required, for each LED.
| LED | State | Explanation | Suggested action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blade error LED | yellow | A system error has occurred on the blade server. | Check the BladeCenter error log, see Problem reporting. |
| Information LED | yellow | Information about a system event has been placed in the Advanced Management Module Event Log. The information LED remains on until turned off by Advanced Management Module or through IBM Director Console. | Check Advanced Management Module to see what the problem is. See the BladeCenter Management Module User's Guide for further information about the error. |
| Activity LED | Green | There is network activity. | No action required. For further information about troubleshooting networks, see Network connection problems. |
| Power-on LED | Flashing rapidly | The service processor on the blade server is communicating with the BladeCenter Management Module. | No action required |
| Flashing slowly | The blade server has power but is not turned on. | Turn on if required | |
| Lit continuously (steady) | The blade server has power and is turned on. | No action required | |
| Not lit. | Blade server not powered. |
|
The blade server must be removed from the BladeCenter unit and the cover removed before you can use the light path LEDs for diagnostics. To activate the light box and the other light path LEDs, press the light path diagnostics switch.

The location of each LED on the system board is shown in the table below.
| LED | Color | Board location | Explanation | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Status LEDs | The status LEDs are listed for reasons of completeness since they are for use by IBM service only and are not normally visible. They are not activated by the light path diagnostics switch. | |||
| Heartbeat | Green | D16 | Indicates the BMC is functional. | |
| Alert | Yellow | D15 | Indicates an error condition has occurred on the system board. | |
| Ethernet 1 activity | Green | D12 | Indicates on-board Ethernet 1 is active and sending or receiving packets. | |
| Ethernet 0 activity | Green | D11 | Indicates on-board Ethernet 0 is active and sending or receiving packets. | |
| BE0_PLL_LOCK | Green | D8 | Indicates the phased lock loop of Cell BE-0 is working. | |
| BE1_PLL_LOCK | Green | D13 | Indicates the phased lock loop of Cell BE-1 is working. | |
| MM_SELECT_A | Green | D19 | Indicates Advanced Management Module A is active. | |
| MM_SELECT_B | Green | D18 | Indicates Advanced Management Module B is active. | |
| Light path LEDs | ||||
| DIMM at I/O BUF 1 error | Yellow | DS9 | There has been a failure in the
I/O DIMM module.
See Figure 27 for the location of each DIMM and its associated LED. |
Either remove or replace the faulty DIMM. Note that if you remove one I/O buffer DIMM you must remove the other. Reboot. |
| DIMM at I/O BUF 2 error | Yellow | DS10 | ||
| System DIMM1 error | Yellow | DS1 | There has been a failure in the
system DIMM module.
See Figure 27 for the location of each DIMM and its associated LED. |
Either remove or replace the faulty DIMM and reboot. See Adding or changing I/O buffer DDR2 memory modules for supported memory configurations. |
| System DIMM2 error | Yellow | DS2 | ||
| System DIMM3 error | Yellow | DS3 | ||
| System DIMM4 error | Yellow | DS4 | ||
| System DIMM5 error | Yellow | DS1 | ||
| System DIMM6 error | Yellow | DS6 | ||
| System DIMM7 error | Yellow | DS7 | ||
| System DIMM8 error | Yellow | DS8 | ||
| Light box LEDs | ||||
| Temperature fault | Yellow | Light box | The blade server has exceeded the operational temperature range. |
If the problem persists, contact your IBM service representative as the system board may need servicing. |
| NMI error (NMI) | Yellow | The NMI pinhole reset on the front panel has been pressed. | Pressing the reset causes the operating system to call the system debugger. | |
| CPU fail | Yellow | One of the Cell BE processors has failed. | Contact your IBM service representative as the system board needs replacement. | |
| System board | Yellow | A critical error has occurred in a component on the system board. | Contact your IBM service representative as the system board may need replacing. | |
| Light path diagnostics | Green | Lights when the light path diagnostics switch is pressed. Indicates that the capacitor is charged and the light path LEDs can light to show any errors. | If this LED does not light then the light
path LEDs cannot function.
Reinstall the blade server in the BladeCenter unit and power on to recharge. If this fails to resolve the problem, there is a problem with the system board and it may need replacement. |
Be aware that the BladeCenter unit automatically reduces the BladeCenter QS22 processor speed if certain conditions are met. One such condition is temperature thresholds being exceeded, for example, when the blade server is running in acoustic mode. This throttling occurs independent of your power configuration. Full processor speed is restored automatically when the conditions that have caused the throttling have been resolved.
| Network connection symptom | Suggested action |
|---|---|
| One or more blade servers are unable to communicate with the network. | Make sure that:
For additional information, see:
Note:
For the latest editions of the IBM BladeCenter documentation,
go to http://www.ibm.com/support/us/en/.
If the problem remains, see Solving undetermined problems. If all the blades cannot communicate with the network, check the network itself for problems. |
| Service processor symptom | Suggested action |
|---|---|
| Service processor reports a general monitor failure. |
If the problem remains, see Solving undetermined problems |
| Symptom | Suggested action |
|---|---|
| You suspect a software problem. |
|
The system firmware is contained in two separate images in the flash memory of the blade server: temporary and permanent. These images are referred to as TEMP and PERM, respectively. The system normally starts from the TEMP image, and the PERM image serves as a backup. If the TEMP image becomes damaged, such as from a power failure during a firmware update, the system automatically starts from the PERM image.
If the TEMP image is damaged, you can recover the TEMP image from the PERM image. See Recovering the TEMP image from the PERM image for further information.
To check whether the system has started from the PERM image, enter:
cat /proc/device-tree/openprom/ibm,fw-bank
A P is returned if the system has started from the PERM image.
To initiate a boot from the TEMP image after the system has booted from the PERM side, complete the following steps:
If the blade server does not restart, you must replace the system board assembly. Contact a service support representative for assistance.
To recover the TEMP image from the PERM image, you must copy the PERM image into the TEMP image. To perform the copy, complete the following steps:
update_flash -r
You might need to update the firmware code to the latest version. See Installing the system firmware for more information on updating the firmware code.
The BladeCenter QS22 can boot from the operating system installation CDs or DVDs to allow the operating system to be installed.
The BladeCenter QS22 can also boot from:
If you wish to perform a standard Bootp/TFTP network boot, please note the following restrictions:
Use Advanced Management Module to configure the required boot mode. See IBM BladeCenter Management Module Installation Guide for more information.
This section provides an overview on how to interpret the console output of the host firmware. The output is grouped into several parts, which are detailed below.
*************************************************************************** QS22 Firmware Starting Check ROM = OK Build Date = Jan 4 2008 11:31:29 FW Version = "QD-1.26.0-0" Press "F1" to enter Boot Configuration (SMS) Press "F2" to boot once from CD/DVD
DDR2 MEMORY INITIALIZATION CPU0 DIMMs: DIMM1=1024MB DIMM2=1024MB DIMM3=n/a DIMM4=n/a CPU0 timings: 800 MHz, CL=6, tRCD=6, tRP=6 CPU0 memory test: ok CPU1 DIMMs: DIMM5=1024MB DIMM6=1024MB DIMM7=n/a DIMM8=n/a CPU1 timings: 800 MHz, CL=6, tRCD=6, tRP=6 CPU1 memory test: ok COMPLETE
SYSTEM INFORMATION Processor = PowerXCell DD1.0 @ 3200 MHz I/O Bridge = Cell BE companion chip DD3.x Timebase = 26666 kHz (internal) SMP Size = 2 (4 threads) Boot-Date = 2008-01-16 11:25 Memory = 4096MB (CPU0: 2048MB, CPU1: 2048MB)
OPEN FIRMWARE
Adapters on 000001460ec00000
00 0800 (D) : 14e4 16a8 network [ ethernet ]
00 0900 (D) : 14e4 16a8 network [ ethernet ]
Adapters on 000001a040000000
00 0000 (B) : 1014 032c pci
Adapters on 000001a240000000
00 0000 (B) : 1014 032c pci
IOBUF1 initializing... no DIMM.
Adapters on 000003460ec00000
00 0800 (D) : 1033 0035 usb-ohci ( NEC uPD720101 )
00 0900 (D) : 1033 0035 usb-ohci ( NEC uPD720101 )
00 0a00 (D) : 1033 00e0 usb-ehci*
Adapters on 000003a040000000
00 0000 (B) : 1014 032c pci
Adapters on 000003a240000000
00 0000 (B) : 1014 032c pci
IOBUF2 initializing... no DIMM.
SB0 Monitor started
SB1 Monitor started
Scan USB...
uDOC not present
Ready
Welcome to Open Firmware
Licensed Internal Code - Property of IBM
(c) Copyright IBM Corp. 2005, 2007 All Rights Reserved.
Cell/B.E. is a trademark of SONY Computer Entertainment Inc.
Type 'boot' and press return to continue booting the system.
Type 'sms-start' and press return to enter the configuration menu.
Type 'reset-all' and press return to reboot the system.
disable nvram logging .. doneThe Operating System now boots unless you have pressed F1 in which case the SMS menu starts. See Using the SMS utility program for further information.
The Dynamic System Analysis (DSA) Preboot diagnostic programs are the primary method of testing the major components of the server. DSA is a system information collection and analysis tool that you can use to provide information IBM service and support to aid in the diagnosis of the system problems. The DSA diagnostic programs come on the IBM Dynamic System Analysis Preboot Diagnostic CD. You can download the CD from http://www.ibm.com/support/us/en if one did not come with your server. As you run the diagnostic programs, text messages are displayed on the screen and are saved in the test log. A diagnostic text message indicates that a problem has been detected and indicates the action you should take as a result of the text message.
The DSA diagnostic programs collect the following information about the following aspects of the system:
The DSA diagnostic programs can also provide diagnostics for the following system components:
Additionally, DSA creates a merged log that includes events from all collected logs.
All collected information can be output as a compressed XML file that can be sent to IBM Service. Additionally, you can view the information locally through a generated text report file. Optionally, the generated HTML pages may be copied to removable media and viewed from a web browser.
To run the diagnostic programs, complete the following steps:
*************************************************************************** QS22 Firmware Starting Check ROM = OK Build Date = Jan 4 2008 11:31:29 FW Version = "QD-1.26.0-0" Press "F1" to enter Boot Configuration (SMS) Press "F2" to boot once from CD/DVD
When you are using the CPU or Memory stress tests, call your IBM service representative if you experience any system instability.
To determine what action you should take as a result of a diagnostic text message, see DSA error messages.
Open firmware memory diagnostic results are output to the SOL connection. They are also logged in NVRAM. All NVRAM logs (more than just OF diags) are collected as part of the DSA merged log.
If the diagnostic programs do not detect any hardware errors but the problem remains during normal server operations, a software error might be the cause. If you suspect a software problem, see the information that comes with your software.
A single problem might cause more than one error message. When this happens, correct the cause of the first error message. The other error messages usually will not occur the next time you run the diagnostic programs.
If there are multiple error codes or light path diagnostics LEDs that indicate a microprocessor error, the error might be in a microprocessor or in a microprocessor socket. See Table 21 for further information about diagnosing microprocessor problems.
If the server stops during testing and you cannot continue, restart the server and try running the diagnostic programs again.
Diagnostic text messages are displayed while the tests are running. A diagnostic text message contains one of the following results:
Additional information concerning test failures is available in the extended diagnostic results for each test.
To view the test log when the tests are completed, issue the view command from the DSA command line interface. DSA collections may also be transferred to an external USB device using the copy command from the DSA command line interface.
The tables below describe the messages that the diagnostic programs might generate and suggested actions to correct the detected problems. Follow the suggested actions in the order given.
| Test | Number | Status | Extended results | Actions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPU stress test | 089-901-xxx | Fail | Test failure |
|
| 089-802-xxx | Abort | System resource availability error | ||
| 089-801-xxx | Abort | Internal program error |
| Test | Number | Status | Extended results | Actions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I2C test | 166-901-xxx | Fail | The BMC indicates a failure in the IPMB bus. |
|
| 166-902-xxx | Fail | The BMC indicates a failure in the memory card bus. |
|
|
| 166-903-xxx | Fail | The BMC indicates a failure in the Ethernet sideband bus. |
|
|
| 166-904-xxx | Fail | The BMC indicates a failure in the main bus. |
|
|
| 166-905-xxx | Fail | The BMC indicates a failure in the pecos bus. | ||
| 166-906-xxx | Fail | The BMC indicates a failure in the BMC private bus. | ||
| 166-907-xxx | Fail | The BMC indicates a failure in the power backplane bus. | ||
| 166-908-xxx | Fail | The BMC indicates a failure in the microprocessor bus. | ||
| 166-910-xxx | Fail | The BMC indicates a failure in the PCIe and Light path diagnostics bus. |
| Test | Number | Status | Extended results | Actions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 166-801-xxx BMC | Abort | BMC I2C test canceled: the BMC returned an incorrect response length. |
|
|
| 166-802-xxx BMC | Abort | BMC I2C test canceled: the test cannot be completed for an unknown reason. | ||
| 166-803-xxx BMC | Abort | BMC I2C test canceled: the node is busy; try later. | ||
| 166-804-xxx BMC | Abort | BMC I2C test canceled: invalid command. | ||
| 166-805-xxx BMC | Abort | BMC I2C test canceled: invalid command for the given LUN. | ||
| 166-806-xxx BMC | Abort | BMC I2C test canceled: timeout while processing the command. | ||
| 166-807-xxx BMC | Abort | BMC I2C test canceled: out of space | ||
| 166-808-xxx BMC | Abort | BMC I2C test canceled: reservation canceled or invalid reservation ID | ||
| 166-809-xxx BMC | Abort | BMC I2C test canceled: request data was truncated. | ||
| 166-810-xxx BMC | Abort | BMC I2C test canceled: request data length is invalid. | ||
| 166-811-xxx BMC | Abort | BMC I2C test canceled: request data field length limit is exceeded. | ||
| 166-812-xxx BMC | Abort | BMC I2C test canceled: a parameter is out of range. | ||
| 166-813-xxx BMC | Abort | BMC I2C test canceled: cannot return the number of requested data bytes. | ||
| 166-814-xxx BMC | Abort | BMC I2C test canceled: requested sensor, data, or record is not present. | ||
| 166-814-xxx BMC | Abort | BMC I2C test canceled: invalid data field in the request. |
|
|
| 166-816-xxx BMC | Abort | BMC I2C test canceled: the command is illegal for the specified sensor or record type | ||
| 166-817-xxx BMC | Abort | BMC I2C test canceled: a command response could not be provided | ||
| 166-818-xxx BMC | Abort | BMC I2C test canceled: cannot execute a duplicated request. | ||
| 166-819-xxx BMC | Abort | BMC I2C test canceled: a command response could not be provided; the SDR repository is in update mode. | ||
| 166-820-xxx BMC | Abort | BMC I2C test canceled: a command response could not be provided; the device is in firmware update mode. | ||
| 166-821-xxx BMC | Abort | BMC I2C test canceled: a command response could not be provided; BMC initialization is in progress | ||
| 166-822-xxx BMC | Abort | BMC I2C test canceled: the destination is unavailable. | ||
| 166-823-xxx BMC | Abort | BMC I2C test canceled: cannot execute the command; insufficient privilege level. | ||
| 166-824-xxx BMC | Abort | BMC I2C test canceled: cannot execute the command. | ||
| 166-000-xxx | Pass |
| Test | Number | Status | Extended results | Actions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Memory stress test | 201-000-xxx | Pass | ||
| 202-802-xx | Fail | General error: memory size is insufficient to run the test. |
|
|
| 202-901-xxx | Fail | Test failure. |
|
|
| 202-801-xxx | Abort | Internal program error. |
|
|
| 202-000-xxx | Pass |
The system firmware displays the progress of the startup process on the serial console from the time that ac power is connected to the system until the operating system login prompt is displayed following a successful operating system startup.
If a serial console is not connected, you can use the Advanced Management Module to monitor the logs and display informational and error messages.
If the firmware encounters an error during the startup process, a message describing the error together with an error code is displayed on the serial console.
There are two types of error, where xxx represents the number of the error code:
There are cases where a message that is informational only is displayed on the serial console.
A complete list of possible messages is given in the section Boot errors and handling.
Checkpoints show the progress of the boot. Each checkpoint is overwritten by the next as the boot process continues. If the boot process stops for any reason, a checkpoint may be displayed. Take note of the checkpoint code and any message, then attempt to reboot the blade server.
If the problem persists, contact your IBM service representative with details of the checkpoint and any message associated with it.
The following sections describe boot errors and actions you can take to resolve these errors.
The following table describes boot list errors.
| Code | Message | Description | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| E3400 | It was not possible to boot from any device specified in the VPD | The firmware found a valid VPD but was not able to find bootable code on any of the devices listed in it. | Use Advanced Management Module Web browser to specify at least
one device that contains bootable code.
From the Advanced Management Module Web interface, choose BladeTasks>Configuration>Boot Sequence. |
| E3401 | Aborting boot, <details> | Boot aborted due to error detected by the low level code. The <details> string provides the error description. | Based on the <details>
string you may have to take an action on faulty hardware or use the Advanced Management Module to
correct the system configuration.
If the problem persists, contact your IBM service representative. |
| E3402 | Aborting boot, internal error. | Boot aborted due to error detected by the low level code. | The exact reason is unknown but could be
a firmware problem.
If the problem persists, contact your IBM service representative. |
| E3403 | Bad executable: <details> | The file loaded from the boot device is not a valid PPC executable ELF file. The <details> string provides more details about the file type. | Using the Advanced Management Module correct the boot device configuration. Select a valid boot device and executable path |
| E3404 | Not a bootable device! | The system cannot load an executable file from this device. | Using the Advanced Management Module correct the boot device configuration. Select a valid boot device and executable path. |
| E3405 | No such device | The specified boot device is currently not present or not ready for access. | Check the hardware device or use the Advanced Management Module to
correct the system configuration.
If the problem persists, contact your IBM service representative. |
| E3406 | Client application returned an error: <details> | The OS or a standalone application returned an error code to the system firmware. The <details> string provides the error description | Based on the <details> string you may have to take an action on faulty hardware or use the Advanced Management Module to correct the system configuration. It may be needed to perform the firmware or OS upgrade to resolve compatibility issues. If the problem persists, contact your IBM service representative. |
| E3407 | Load failed | Load or boot failed to load requested file from the device. This is informational message and may be preceded by one or more other error messages. | Based on the preceding error messages you may have to take an action on faulty hardware or use the Advanced Management Module to correct the system configuration |
| E3408 | Failed to claim memory for the executable | An attempt to load executable file from the boot device failed due to insufficient memory or firmware problem. | Verify that loaded file was indeed the right executable intended to boot this system. If not, using the Advanced Management Module correct the system configuration. Otherwise, contact your IBM service representative. You may need to add more memory to the system or to perform the firmware upgrade. |
| E3409 | Unknown FORTH Word | Internal code error, or compatibility issue. | Contact your IBM service representative. You may need to perform the firmware upgrade. |
| E3410 | Boot list successfully read from VPD but no useful information received. | The firmware found a valid VPD but was not able to find bootable code on any of the devices listed in it. | Use Advanced Management Module Web browser to specify at least
one device that contains bootable code.
From the Advanced Management Module Web interface, choose BladeTasks>Configuration>Boot Sequence. |
| W3411 | Client application returned. | Loaded OS or standalone application returned to firmware. This may be a normal condition or firmware could not detect any error issued by the client application. Booting from the boot-device list will be interrupted at this stage and no further attempts to boot from devices in the list will be made. | None needed. If boot (e.g. yaboot) exited because of need to boot from different device in the list, either boot manually from the firmware (ok) prompt or, using the Advanced Management Module, change the boot device order in the system configuration. |
| E3420 | Boot list could not be read from VPD. | The firmware found an invalid VPD. Possibly it has been corrupted by the system software. | The VPD must be rewritten. Use the Advanced Management Module Web
browser to specify at least one device that contains bootable code.
From the Advanced Management Module Web interface, choose BladeTasks>Configuration>Boot Sequence. If the problem persists, contact your IBM service representative. |
The following table describes system firmware errors that can occur if there have been problems after an update.
| Code | Message | Description | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| E4000 | (RTAS Flash) unknown flash chip version | The flash update code does not support the onboard boot ROM flash chip. | Contact your IBM service representative as the system board may need replacing. |
| E4010 | Platform check failed for image | The firmware image does not match the hardware platform. | Check the firmware image and ensure you
have the right image for the BladeCenter QS22. See Using the SMS utility program.
If the image is incorrect, download and install the correct image from http://www.ibm.com/support/us/en/. See Updating the system and BMC firmware for further information. |
| E4020 | (RTAS flash) image corrupted (CRC) | The image for a system firmware update is corrupted. | Download the image again
and reapply the update.
If this does not resolve the problem, apply an image from a different source. |
The following table describes system memory initialization errors that can occur during boot.
| Code | Message | Description | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| E1100 | Incompatible DIMM in slot x.
Disabling slots x and y.
where x is the slot containing the incompatible DIMM and y is the slot containing its pair. |
Incompatible DIMM. DIMM does not match technical
requirements of the memory controller.
Note:
Both the offending
DIMM and its pair are disabled. System DIMM must operate in pairs. |
Replace the DIMM with a supported DIMM.
See Parts listing for details of supported DIMMs. |
| W1110 | Unsupported DIMM in slot x.
where x is the slot containing the unsupported DIMM. |
Unsupported DIMM. DIMM is within technical requirements of memory controller but is untested. | Replace the DIMM with a supported DIMM.
See Parts listing for details of supported DIMMs. |
| E1120 | Unsupported plugging: No pair in slots x and
y. Disabling slots.
where x and y form the pair of slots on a given channel. |
Plugging rule violation. No pair plugged on a given channel. | Check DIMM configuration. See Adding or changing system memoryfor details of permitted configurations. |
| W1130 | Unsupported plugging.
This message appears with one of the following informational messages: |
Plugging sequence violation. DIMMs are not plugged in supported sequence | Check DIMM configuration. See Adding or changing system memory details of permitted configurations. |
| No local memory on CPU1 | No local memory on IBM PowerXCell 8i processor 1. There should be DIMMs on IBM PowerXCell 8i processor 1, but this is not the case. | ||
| No local memory on CPU2 | No local memory on IBM PowerXCell 8i processor 2. There should be DIMMs on IBM PowerXCell 8i processor 2, but this is not the case. | ||
| Slots 1 and 2 should both have DIMMs plugged | Either slot 1 or slot 2 has no DIMMs plugged, but this should not be the case. | ||
| Slots 5 and 6 should both have DIMMs plugged | Either slot 5 or slot 6 has no DIMMs plugged, but this should not be the case. | ||
| Slots [3,7] and [4,8] should have both DIMMs plugged | Slots 3,4,7,8 are not completely plugged.
Slots 1,2,5,6 are plugged, additional slots are plugged, but not all of 3,4,7,8. |
||
| E1140 | Slots x and y are plugged with different DIMM types. Disabling slots. | The type or the speed bin of the two DIMMs on a given channel differs. | Replace the DIMM with a supported DIMM.
See Parts listing for details of supported DIMMs. |
| E1150 | DIMMs in slots x and y have different amount of ranks. Disabling slots a and b | DIMM rank count on channel differs.
The number of ranks of the two DIMMs on a given channel differs. |
Replace the DIMMs with ones of the same type.
See Parts listing for details of supported DIMMs. |
| E1160 | DIMMs on CPUx have different types on channel 1 and 2. Disabling slots a and b. | DIMM types across channels differ.
The type or speed bin of the DIMMs on CH0 is different than the type of the DIMMs on CH1. |
Replace the DIMMs with ones of the same type.
See Parts listing for details of supported DIMMs. |
| W1170 | DIMMs on CPux have different speed bins on channel 1 and 2. | DIMM speed bins across channels differs.
Speed bins on Chx are greater than those on CHy |
Replace the DIMMs with ones of the same type.
See Parts listing for details of supported DIMMs. |
| W1180 | DIMMs on CPux have different rank count on channel 1 and 2. Truncating slots a and b. | DIMM rank count across channels differs | Replace the DIMMs with ones of the same type.
See Parts listing for details of supported DIMMs. |
| E1200 | Error during memtest.
This message appears with one of the following informational messages: |
Memory test failed | |
| Detected MIC SRAM parity error. | MIC SRAM parity failed during memtest.
MIC detected a parity error in an internal buffer. |
||
| Detected MIC Data write error. | MIC DERR during memtest
MIC received a DERR condition from another on chip unit upon a write request from that unit. |
||
| Detected single-bit ECC error (recoverable) on DIMM x or DIMM y. | A correctable error occurred during memtest. | Replace the DIMM where the error occurred with
a supported DIMM.
See Parts listing* for details of supported DIMMs. |
|
| Detected multi-bit ECC uncorrectable error on DIMM x or DIMM y. | An uncorrectable error occurred during memtest | Replace the DIMM where the error occurred with
a supported DIMM.
See Parts listing for details of supported DIMMs. |
|
| Stuck data bit on DIMM x. | Stuck data bit during memtest.
One or more data lanes failed in the stuck bit test. |
Replace the DIMM where the error occurred with
a supported DIMM.
See Parts listing for details of supported DIMMs. |
|
| Stuck address bit on DIMM x. | Stuck address bit during memtest.
One or more address lanes failed in the stuck bit test. |
Replace the DIMM where the error occurred with
a supported DIMM.
See Parts listing for details of supported DIMMs. |
|
| E1300 | No memory available at address zero. Aborting system boot. | No memory is assigned to address 0. Due to error E1100 all memory attached to CPU with address zero must be disabled. | Replace the DIMM where the error occurred with
a supported DIMM.
See Parts listing for details of supported DIMMs. |
| W1400 | Memory hole between physical address x and y | Memory hole.
Due to error E1100 a portion of the predetermined physical address map (configuration ring) is unavailable, leaving a memory hole in the address map. |
Replace the DIMM where the error occurred with
a supported DIMM.
See Parts listing for details of supported DIMMs. |
| E1500 | Bad memory configuration. Aborting system boot | Bad configuration.
Due to occurrences of errors E1100, E1120, E1140, E1150 the BMC cannot power on the system. |
Check DIMM configuration and correct where necessary. See Adding or changing system memory for details of permitted configurations. |
| W1700 | Multiple attempts needed to reset DQS latches on CPUx. | DQS reset problems.
Firmware needed multiple attempts to ensure that the DQS latches were properly put in reset. |
IBM PowerXCell 8i informational message |
| W1800 | Unable to reset DQS latches on CPUx. | DQS reset error.
Firmware exceeded maximum attempts to ensure that the DQS latches were properly put in reset. |
IBM PowerXCell 8i informational message |
The following table describes boot list errors. These may occur when booting from a bootable CD or DVD.
| Code | Message | Description | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| E5000 | (USB) Media or drive not ready for this blade. | The media tray is not accessible for boot. | Verify that the media tray is assigned to
the blade and that the media is configured correctly.
If this does not resolve the problem, check the other blade servers. If they cannot access the media, there may be a problem with the BladeCenter unit. See the documentation that comes with the BladeCenter unit for further information. |
| E5010 | (USB) No Media Found! Please check for the drawer/inserted media. | Media is not inserted or the drawer of the media tray is open. | Ensure that there is a bootable CD or DVD in the tray and that the drawer is closed. |
| E5020 | (USB) Unknown media format. | The media is not recognized by the firmware. | Insert a suitable bootable CD. |
| E5030 | (USB) Device communication error | Firmware cannot communicate with the BladeCenter USB devices. | This could be a firmware or physical hardware
problem. Check:
Finally, power down then reboot the blade. If this does not help resolve the problem, contact your IBM service representative. |
| E5040 | (USB) Device transaction error. <command>
Note:
<command> indicates
the command in progress when the transaction error occurred. This
information may not always be available. |
The drive showed an error during data transfer. |
|
The following table describes the network boot errors.
These error messages only appear if you have installed the optional SAS expansion card.
| Code | Message | Description | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| E4303 | LSISAS1064 controller initialization failed. | The blade server firmware was not able to initialize the controller. This could indicate a hardware, blade server firmware, or SAS expansion card firmware problem. |
|
| E4304 | LSISAS1064 controller operation failed. | The blade firmware was not able to bring the controller to an operational state. This could indicate a hardware, blade server firmware, or SAS expansion card firmware problem. | |
| E4305 | LSISAS1064 port failed. | The blade firmware could not enable the SAS port. This could indicate a hardware, blade server firmware, or SAS expansion card firmware problem. | |
| E4307 | LSISAS1064 network topology read failed. | The blade server firmware was not able to discover the SAS topology. This could indicate a hardware, blade server firmware, or SAS expansion card firmware problem. | |
| E4308 | SAS disk device node not found! | The Open Firmware Device Tree (see IEEE 1275) become corrupted. It might indicate a blade firmware problem. |
|
| E4309 | SAS disk (@<Bus>,<ID>,<LUN>): SAS address not found! | The Open Firmware Device Tree (see IEEE 1275)
is corrupted. This might indicate a blade server firmware problem.
Note that it is likely that blade firmware was not able to read a
remote disk as well (see error #E430B).
The <Bus>, <ID>, and <LUN> values determine the disk's Open Firmware Device Tree unit address (see IEEE 1275). Sample error message: E4309 SAS disk (@0,3,0): SAS address not found! The Open Firmware Device Tree node name is /axon@10000000000/plb5/plb4/pcix@4000004600000000/scsi@2/disk@0,3,0. The disk is located at Bus#0, ID#3, and LUN#0. |
|
| E430A | SAS disk block size not found! | The Open Firmware Device Tree (see IEEE 1275) has become corrupted. This might indicate a blade server firmware problem. |
|
| E430B | SAS disk (@<Bus>,<ID>,<LUN>): SAS Address xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx, LUN#<LUN> | The blade firmware was not able to read a disk. The error might be due
to connectivity, SAS switches, disk, attached storage, hardware, blade firmware, or SAS
Expansion Card firmware problem(s).
Output: The <Bus>, <ID>, and <LUN> values are determine the disk's Open Firmware Device Tree unit address (see IEEE 1275). The xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx value determines the SAS address of device containing the disk. If a disk is a physical device then the SAS address is the identifier of disk itself. If a disk is a volume within a RAID controller then the SAS address is identifier of the RAID controller. The <LUN> is disk logical unit number. Note:
though the logical unit
number is printed explicitly and within the unit address, it is always
the same value.
Sample error message: E430B SAS disk (@0,3,0): SAS Address 50:01:0b:90:00:42:8a:ee, LUN#0 The Open Firmware Device Tree node name is /axon@10000000000/plb5/plb4/pcix@4000004600000000/scsi@2/disk@0,3,0. The disk is located at Bus#0, ID#3, and LUN#0. The SAS address of device containing disk is 50:01:0b:90:00:42:8a:ee. The logical unit number is zero. |
|
| E430C | LSISAS1064 Not Operational State | The controller operation has failed. This could
indicate a hardware, blade server firmware, or SAS Expansion Card
firmware problem.
Note:
The blade firmware tries to recover
the controller when this condition met. |
|
| E430D | LSISAS1064 ambiguous device characteristics obtained | The blade firmware was obtained a weird or ambiguous controller response. This could indicate a hardware, blade server firmware, or SAS Expansion Card firmware problem. | |
| E430E | LSISAS1064 device characteristics read failed | The blade firmware could not obtain device operational or static characteristics. This could indicate a hardware, blade server firmware, or SAS Expansion Card firmware problem. | |
| E430F | Device Tree node creation failed | The blade server firmware was not able to create a device tree node. This might indicate a blade server firmware problem. |
|
| E4310 | LSISAS1064 IR Failed to retrieve parameters for device | LSI Integrated RAID disk characteristics read failed. The error might be due to connectivity, SAS switches, BladeCenter S local SAS disk, hardware, blade firmware, or SAS Expansion Card firmware problems. |
|
| E4311 | LSISAS1064 IR Page #0 read failed | ||
| E4312 | LSISAS1064 IR Page #1 read failed | ||
| W4341 | No SAS Switch in Bay 3 | No SAS Connectivity Module in bay 3 detected. This could indicate that the module is failed, absent, or inappropriately configured.When using a BC-S chassis, the placement of the SAS Connectivity Module is critical. Single Switch Predefined Zones in BC-S require the module in bay 3. For the BC-H chassis, you do not have to install a module in bay 3. However, installing the module in bay 3 first, then in bay 4 ensures the first port of the IBM SAS Expansion Card is used. |
|
| W4342 | Unsupported SAS Phys have an established link | This could indicate a hardware or SAS Expansion Card firmware problem SAS Expansion Card has four SAS Phys, sometimes referred as ports. Phy 0 and Phy 1 only are physically connected to SAS Connectivity Modules in bay 3 and bay 4. As Phy 2 and Phy 3 are idle, no connections via these Phys are expected. |
|
| W4344 | LSISAS1064 IR ambiguous maximum LBA value | LSI Integrated RAID disk size requests reported inconsistent values. The error might be due to connectivity, SAS switches, BladeCenter S local SAS disk, hardware, blade firmware, or SAS Expansion Card firmware problems. |
|
| W4345 | Duplicate reply-type Reply | The blade server firmware received an unexpected
duplicate address-type or context-type reply. This could indicate
a hardware, blade server firmware, or SAS expansion card firmware
problem.
reply-type is Address for an address-type reply and Context for a context-type reply. |
|
These error messages only appear if you have installed optional I/O DIMM.
| Code | Message | Description | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| E2001 | Incompatible DIMM type (not DDR2). | The DIMM is not a DDR2 DIMM. | Replace the DIMM with a DIMM of type DDR2. |
| E2002 | Incompatible DIMM type (not registered type). | The DIMM is not a registered DIMM. | Replace the DIMM with a DIMM of type "registered". |
| E2011 | Incompatible DIMM type (maximum DIMM frequency too slow). | The maximum I/O-frequency of the DIMM is slower than memory controller's frequency. | Replace the DIMM with a DIMM allowing an I/O-frequency of at least 333MHz. |
| E2012 | Incompatible DIMM type (CAS Latency). | The DIMM does not provide a CAS Latency setting for an I/O-frequency of 333 MHz or the configuration data is inconsistent. | Replace the DIMM with a DIMM with correct configuration data. |
| E2013 | Incompatible DIMM type (Burst Length). | The DIMM does not support a Burst Length of 4. | Replace the DIMM with a DIMM supporting a Burst Length of 4. |
| E2014 | Incompatible DIMM type (wrong bank count). | The DIMM has a bank count different from 4 and 8. | Replace the DIMM with a DIMM with a bank count of 4 or 8. |
| E2021 | Incompatible DIMM type (DIMM data width). | The DIMM's the data width is different from 36 and 72. | Replace the DIMM with a DIMM with a data width of 36 or 72. |
| E2022 | Incompatible DIMM type (SDRAM data width). | The DIMM's data-lanes are organized other than "by 8". | Replace the DIMM with a DIMM with an SDRAM data width of 8 lanes. |
| E2031 | Data error. | The DIMM is defective. | Replace the DIMM with a new one. |
| E2032 | Address line error. | The DIMM is defective. | Replace the DIMM with a new one. |
The following table shows the warning messages that may appear:
| Code | Message | Description | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| W2081 | Unsupported DIMM type (not 1 GB). | The DIMM has a size different from 1 GB. | Replace the DIMM with a DIMM of size 1 GB to avoid compatibility problems. |
| W2082 | Unsupported DIMM type (CAS Latency z instead of 5). | The DIMM is operated with CAS Latency z, but only a CAS Latency of 5 is supported. | Replace the DIMM with a DIMM with a CAS Latency of 5 for an I/O frequency of 333 MHz to avoid compatibility problems. |
| W2083 | Unsupported DIMM type (contains more data than program buffer). | The SPD of the DIMM contains more data elements than needed. | Replace the DIMM with an SPD of 128 bytes to avoid compatibility problems. |
The following table shows informational messages.
| Code | Message | Description | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| No DIMM. | The socket is not populated. | Insert a DIMM into the empty socket to make full use of the I/O-buffer capability. |
In addition to appearing on the console, messages are also written to the Advanced Management Module log. The table below lists the messages.
| Message | Severity | Description | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blade memory fault: Exxxx on
JIOBUFyy.
Where Exxxx is the error number shown in the table Table 16 and JIOBUFyy is the slot number of the affected I/O buffer DIMM |
Error | An error occurred while initializing one I/O-buffer memory module. | See the console output for more details and for the affected DIMM. |
| Unsupported I/O Buffer DIMM type: Wxxxx on JIOBUFyy.
Where Wxxxx is the warning number shown in table Table 17and JIOBUFyy is the slot number of the affected I/O buffer DIMM |
Warning | An I/O-buffer memory module with correct but unsupported properties was found. | See the console output for more details and for the affected DIMM. |
The following table describes other error messages that can be displayed.
| Code | Message | Description | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| E1001 | Boot ROM CRC failure | The firmware image was found to be inconsistent during bootup. The inconsistency might be due to image corruption during flash update or might indicate a hardware problem. | The boot watchdog triggers. Reject the malfunctioning flash image as described in Recovering the TEMP image from the PERM image. Power down then reboot the blade. If the problem persists, contact your IBM service representative as the system board assembly may need replacement. |
| E1002 | System memory could not be initialized | The firmware encountered an error during the memory initialization. | The boot watchdog automatically boots the system from the permanent flash side. The malfunctioning firmware image should be rejected as described in Recovering the TEMP image from the PERM image. Power down then reboot the blade. If the problem persists, contact your IBM service representative as the system board assembly may need replacement. |
| E1003 | Firmware image incomplete | The firmware detected missing components and cannot continue execution. | The boot watchdog automatically boots the system from the permanent flash side. The malfunctioning firmware image should be rejected as described in Recovering the TEMP image from the PERM image. Power down then reboot the blade. If the problem persists, contact your IBM service representative as the system board assembly may need replacement. |
| E1004 | Unspecified Internal Firmware Error | The firmware encountered an unexpected error condition. | The boot watchdog automatically boots the system from the permanent flash side. The malfunctioning firmware image should be rejected as described in Recovering the TEMP image from the PERM image. Power down then reboot the blade. If the problem persists, contact your IBM service representative as the system board assembly may need replacement. |
The following is a description of the BMC firmware messages that are sent to the Advanced Management Module. Use the Advanced Management Module Web interface to view them.
No codes are associated with these messages. However, the status column indicates their severity.
There are three levels of severity:
| Message | Severity | Event | Automatic Action by BMC | Action required by user |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature events | ||||
| Blade x throttled.
where x is the number of the blade server in the BladeCenter unit. |
Information |
Acoustic mode IBM PowerXCell 8i processor 1 Temp above Warning Temperature (>78 °C) Standard mode IBM PowerXCell 8i processor 1 Temp above Warning Temperature (>90 °C) |
Throttle (Reduce Frequency).
This is a BladeCenter unit operation which reduces processor speed on the blade server concerned until the temperature has dropped to normal levels. |
No action required. |
| Processor 1 (CPU 1 Chip) over warning threshold.
Reading: x, Threshold: 88.00. where x is the temperature of the processor. |
Warning |
Standard mode IBM PowerXCell 8i processor 1 Temp above Warning Temperature (>88 °C) |
Advanced Management Module increases blower speed. | |
| Processor 2 (CPU 2 Chip) over warning threshold.
Reading: x, Threshold: 88.00. where x is the temperature of the processor. |
Warning |
Standard mode IBM PowerXCell 8i processor 2 Temp above Warning Temperature (>88 °C) |
Advanced Management Module increases blower speed. | |
| Processor 1 (CPU 1 Chip) over critical
threshold.
Reading: x, Threshold: 100.00. where x is the temperature of the processor. |
Error | IBM PowerXCell 8i processor 1 Temp above Shut-Off Temperature ( 100°C) | Power Off
The temperature of the processor has reached a critical level. |
|
| Processor 2 (CPU 2 Chip) over critical threshold.
Reading: x, Threshold: 100.00. where x is the temperature of the processor. |
Error | IBM PowerXCell 8i processor 2 Temp above Shut-Off Temperature ( 100°C) | Power Off
The temperature of the processor has reached a critical level. |
|
| Proc/IO module 1 (IO Bridge 1 Chip) over
warning threshold.
Reading: x, Threshold: 98.00. where x is the temperature of the Proc/IO module. |
Warning |
Standard mode IBM PowerXCell 8i companion chip 1 Temp above Warning Temperature (>98 °C) |
Advanced Management Module increases blower speed. | No action required. |
| Proc/IO module 2 (IO Bridge 2 Chip) over
warning threshold.
Reading: x, Threshold: 98.00. where x is the temperature of the Proc/IO module. |
Warning |
Standard mode IBM PowerXCell 8i companion chip 2 Temp above Warning Temperature (>98 °C) |
Advanced Management Module increases blower speed. | |
| Proc/IO module 1 (IO Bridge 1 Chip) temperature over non-recoverable threshold. | Error | IBM PowerXCell 8i companion chip 1 Temp above Shut-Off Temperature (100°C) | Power Off
The temperature of the system board has reached a critical level. |
|
| Proc/IO module 2 (IO Bridge 2 Chip) temperature over non-recoverable threshold. | Error | IBM PowerXCell 8i companion chip 2 Temp above Shut-Off Temperature (100°C) | Power Off
The temperature of the system board has reached a critical level. |
|
| IBM PowerXCell 8i events | ||||
| CPU 1 internal fault | Error | Processor Failure IBM PowerXCell 8i processor 1 (Checkstop) | Reboot | There may be a problem with the system board. If problem persists, please contact IBM service. |
| CPU 2 internal fault | Error | Processor Failure IBM PowerXCell 8i processor 2 (Checkstop) | Reboot | There may be a problem with the system board. If problem persists, please contact IBM service. |
| CPU 1 Fault + "Init Failed #x" where x is the number of the error condition | Error | Failure Initializing IBM PowerXCell 8i processor 1 or IBM PowerXCell 8i companion chip 1 | Power Off | Reboot. If the problem persists, the blade needs to be replaced. |
| CPU 2 Fault | Error | Failure Initializing IBM PowerXCell 8i processor 2 or IBM PowerXCell 8i companion chip 2 | Power Off | |
| Processor 1 (CPU 1/2 VCORE) over recommended voltage | Warning | IBM PowerXCell 8i processor 1 over recommended Voltage (1,25V) | None | No action required. |
| Processor 1 (CPU 1/2 VCORE) under recommended voltage | Warning | IBM PowerXCell 8i processor 1 under recommended Voltage (0,92V) | None | |
| Processor 2 (CPU 1/2 VCORE) over recommended voltage | Warning | IBM PowerXCell 8i processor 2 over recommended Voltage (1,25V) | None | |
| Processor 2 (CPU 1/2 VCORE) under recommended voltage | Warning | IBM PowerXCell 8i processor 2 under recommended Voltage (0,92V) | None | |
| Planar events | ||||
| System board, voltage (Planar Fault) occurred | Information | Voltage fault | None | No action required |
| Planar voltage fault + "Voltage Fault #x", where x is a bit field showing the state of all the voltage signals | Error | Voltage fault | Power off | Reboot. If the error condition continues, report the exact error message to IBM service. |
| System board, voltage (Out of Range) occurred | Information | Voltage+-10% (not BE voltage) | None | No action required |
| DIAGS: Voltage Fault: 0003557F | Error | Voltage fault | Power off | Reboot. If the error condition continues, report the exact error message to IBM service. |
| System board voltage (planar fault) occurred | Error | Voltage fault | Power off | |
| Battery errors | ||||
| Battery 1 (Battery Status) failed | Error | Battery has no charge. | None | Replace battery |
| Modular flash drive errors | ||||
| Drive bay 1, hard drive (ModFD Error) fault | Error | A fault has occurred with the modular flash drive. | Remove and reseat the modular flash drive. Reboot.If the error condition continues, replace the modular flash drive with a similar unit and reboot.If this does not correct the problem, contact IBM service. | |
| Firmware progress events | ||||
| FW/BIOS, firmware progress (Pri FW Corrupt) system board hang | Error | An error has occurred on the system board during boot. | Blade reboots | If the error persists, contact IBM service. |
| FW/BIOS, firmware progress (Pri FW Corrupt) no system memory | Error | No system memory was found | Blade does not power on | Add system memory, or reseat existing system memory. Reboot. |
| FW/BIOS, firmware progress (Pri FW Corrupt) no usable system memory | Error | System memory was found, but is unusable | Blade does not power on | Check supported memory configurations. See Adding or changing system memory for further information. |
| Memory subsystem | ||||
| Memory device x (DIMM x uncorrectable ECC memory errorwherex is the number of the affected DIMM. | Error | A system DIMM or an I/O buffer DIMM has returned an uncorrectable error. | The affected memory channel is disabled. If the error concerns and I/O buffer DIMM, both I/O buffer DIMMs are disabled. | Replace the affected DIMM. If the problem continues, contact IBM service. |
| Memory device x (DIMM x memory disabledwherex is the number of the affected DIMM. | Error | A system DIMM or an I/O buffer DIMM has returned an uncorrectable error. | The affected memory channel is disabled. If the error concerns and I/O buffer DIMM, both I/O buffer DIMMs are disabled. | |
| Blade memory fault. Memory device x+1 (DIMM x+1 Err) uncorrectable ECC memory error. Memory device x (DIMM x Err) uncorrectable ECC memory error. Processor y (CPU y Status) internal error. | Error | Checkstop due to memory fault. | Replace the affected pair of DIMMs x and x+1 | |
| Memory bank y, memory (DIMM x or x+1 PFA) predictive failure | Error | Predictive failure on memory channel y for main memory of IBM PowerXCell 8i. | Replace the affected pair of DIMMs x and x+1 | |
| Memory device y, memory (IOBUF x PFA) predictive failure | Error | Predictive failure on buffer memory IOBUFx of the IBM PowerXCell 8i companion chip. | Replace DIMM IOBUFx | |
| Other events | ||||
| Front panel critical Interrupt | Error | NMI reset button on Front panel pressed | Soft-Reset | None. This is a user-initiated action. |
| Firmware BIOS ROM Corruption detected | Warning | Boot WDT Timeout (Firmware Corrupted) | Reboot & Switch to the permanent flash side | Reinstall TEMP image. See Recovering the system firmware code for further information. |
| PCI-X card not supported | Error | DIAGS: Invalid PCI-X Card | None | No power on, PCI-X expansion card needs to be replaced |
| Recovery messages | ||||
| Recovery Proc/IO module 1 (IO Bridge 1 Chip) temperature over non-recoverable threshold. | Information | The original problem has been corrected and the component has been restored to full operability. | ||
| Recovery Proc/IO module 1 (IO Bridge 1 Chip) temperature over warning | Information | |||
| Recovery Blade x throttled | Information | |||
| Recovery Processor 1 (CPU 1 Chip) temperature over warning threshold. | Information | |||
| Recovery Battery 1 (Battery Status) low | Information |
The following messages are placed in the Advanced Management Module error log.
The system halts if any of the errors listed below occur.
| Message | Severity | Event | Lightpath LED | Action | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIAGS: SB1 NMI: PCI-X | Error | Cell BE companion chip 1 indicates an error on its PCI-X bus | NMI Error | Reboot. If the system does not reboot or the problem persists, contact IBM service with details of the problem and the error code. | |
| DIAGS: SB2 NMI: PCI-X | Error | Cell BE companion chip 2 indicates an error on its PCI-X bus | NMI Error | ||
| DIAGS: SB1 NMI: PCI-E P00 | Error | Cell BE companion chip 1 indicates an error on PCIe Channel 0 | NMI Error | ||
| DIAGS: SB2 NMI: PCI-E P00 | Error | Cell BE companion chip 2 indicates an error on PCIe Channel 0 | NMI Error | ||
| DIAGS: SB1 NMI: PCI-E P01 | Error | Cell BE companion chip 1 indicates an error on PCIe Channel 1 | NMI Error | ||
| DIAGS: SB2 NMI: PCI-E P01 | Error | Cell BE companion chip 2 indicates an error on PCIe Channel 1 | NMI Error | ||
| DIAGS: SB1 NMI: DIMM 00 | Error | Cell BE companion chip 1 indicates an error on JDIMM 00 | NMI Error | ||
| DIAGS: SB2 NMI: DIMM 01 | Error | Cell BE companion chip 1 indicates an error on JDIMM 01 | NMI Error | ||
Firmware logs and Firmware settings are located in the system's Non-Volatile Random Access Memory (NVRAM). In the case of an error where IBM support is needed, complete the following steps to provide the firmware log information:
cat /dev/nvram > /tmp/QS22-fw-nvram.img
tar cvfz QS22-error-log-<customer>-<date>.tgz \ /tmp/PROBLEM.txt /tmp/QS22-fw-nvram.imgwhere:
The problem description must added to/tmp/PROBLEM.txt together with the following information:
If the blade server is inoperative, use the information in this section.
If you suspect that a software problem is causing failures (continuous or intermittent), see Software problems.
Check the LEDs on all the power supplies of the BladeCenter unit in which the blade server is installed. If the LEDs indicate that the power supplies are working correctly and reseating the blade server does not correct the problem, complete the following steps:
If the problem is solved when you remove the device from the blade server but the problem recurs when you reinstall the same device, suspect the device; if the problem recurs when you replace the device with a different one, suspect the system board. Have a trained service technician replace the system board assembly.
If you suspect a networking problem and the blade server passes all the system tests, suspect the network switch. However, the problem may concern the network itself and be external to the system.
See Appendix B. Getting help and technical assistance for information about calling IBM for service.
When you call for service, have as much of the following information available as possible:
You can solve some problems by comparing the configuration and software setups between working and nonworking servers. When you compare servers to each other for diagnostic purposes, consider them identical only if all the following factors are exactly the same in all the blade servers:
Use the System Management Services (SMS) utility to perform a variety of configuration tasks on the BladeCenter QS22 blade server.
Start the SMS utility to configure the blade server.
QS22 Firmware Starting Check ROM = OK Build Date = Jan 4 2008 11:31:29 FW Version = "QD-1.26.0-0" Press "F1" to enter Boot Configuration (SMS) Press "F2" to boot once from CD/DVD DDR2 MEMORY INITIALIZATION CPU0 DIMMs: DIMM1=4096MB DIMM2=4096MB DIMM3=4096MB DIMM4=4096MB CPU0 timings: 800 MHz, CL=6, tRCD=6, tRP=6Press F1 to enter the SMS menu.
Select SMS tasks from the SMS utility main menu. Choices on the SMS utility main menu depend on the version of the firmware in the blade server. Some menu choices might differ slightly from these descriptions.
PowerPC Firmware Version QD0123000 SLOF-SMS 1.1 (c) Copyright IBM Corp. 2007 All rights reserved. -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Main Menu 1. Select Language 2. Setup Remote IPL (Initial Program Load) 3. Change SCSI Settings 4. Select Console 5. Select Boot Options 6. Firmware Boot Side Options 7. Progress Indicator History 8. FRU Information 9. Change SAS Boot Device
If a device that you are trying to select (such as a USB CD drive in the BladeCenter media tray) is not displayed in the Select Device Type menu, select List all Devices and select the device from that menu.
Select this choice to change the language that is used to display the SMS menus. A screen similar to the following appears:
PowerPC Firmware Version QD0123000 SLOF-SMS 1.1 (c) Copyright IBM Corp. 2007 All rights reserved. -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select Language 1. ISO8859-1 English (United States) * -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Navigation Keys: M = return to Main Menu N = Next page of list ESC key = return to previous screen X = eXit System Management Services -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Type menu item number and press Enter or select Navigation key :
At present, English (United States) is the only available language.
Select this to configure a network adapter for networks that use static IP addresses or TFTP only. By default the QS22 uses DHCP, in which case no changes should be made.
The screen is a similar to:
PowerPC Firmware Version QD0123000 SLOF-SMS 1.1 (c) Copyright IBM Corp. 2007 All rights reserved. -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- NIC Adapters (NET) 1. /axon@10000000000/plb5/plb4/pcix@4000004600000000/ethernet@1 2. /axon@10000000000/plb5/plb4/pcix@4000004600000000/ethernet@1,1 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Navigation Keys: M = return to Main Menu ESC key = return to previous screen X = eXit System Management Services -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Type menu item number and press Enter or select Navigation key :
To view the Network Parameters screen type the number of the adapter you wish to configure and press Enter. A screen similar to the following appears:
PowerPC Firmware Version QD0123000 SLOF-SMS 1.1 (c) Copyright IBM Corp. 2007 All rights reserved. -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Network Parameters NET /axon@10000000000/plb5/plb4/pcix@4000004600000000/ethernet@1 1. IP Parameters 2. Adapter Configuration 3. Ping Test 4. Advanced Setup: DHCP -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Navigation Keys: M = return to Main Menu ESC key = return to previous screen X = eXit System Management Services -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Type menu item number and press Enter or select Navigation key :
Type the number of the menu item and press Enter.
This allows you to configure IP for the network adapter to use static IP addresses or TFTP. You should not change these setting if you use DHCP, which is the default.
PowerPC Firmware Version QD0123000 SLOF-SMS 1.1 (c) Copyright IBM Corp. 2007 All rights reserved. -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- IP Parameters NET /axon@10000000000/plb5/plb4/pcix@4000004600000000/ethernet@1 1. Client IP Address [000.000.000.000] 2. Server IP Address [000.000.000.000] 3. Gateway IP Address [000.000.000.000] 4. Subnet Mask [255.255.255.000] -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Navigation Keys: M = return to Main Menu ESC key = return to previous screen X = eXit System Management Services -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Type menu item number and press Enter or select Navigation key :
Select an item from the list and enter the appropriate address and subnet mask. Press Enter when you have finished each item. To save the information and return to the Main Menu, press M. If you wish to cancel and return to the main menu, press Esc.
This allows you to set network parameters for the adapter.
PowerPC Firmware Version QD0123000 SLOF-SMS 1.1 (c) Copyright IBM Corp. 2007 All rights reserved. -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Adapter Configuration NET /axon@10000000000/plb5/plb4/pcix@4000004600000000/ethernet@1 1. Speed, Duplex 2. Spanning Tree Enabled 3. Protocol -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Navigation Keys: M = return to Main Menu ESC key = return to previous screen X = eXit System Management Services -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Type menu item number and press Enter or select Navigation key :
Do not change these settings unless required by your network. The defaults are:
Only change this if your network uses the Spanning-Tree Protocol link management protocol.
IEE 802.3 is the only other option.
This enables you to verify the static IP addresses you have set.
PowerPC Firmware Version QD0123000 SLOF-SMS 1.1 (c) Copyright IBM Corp. 2007 All rights reserved. -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Ping Test NET /axon@10000000000/plb5/plb4/pcix@4000004600000000/ethernet@1 Speed, Duplex: auto, auto Client IP Address [000.000.000.000] Server IP Address [000.000.000.000] Gateway IP Address [000.000.000.000] Subnet Mask [255.255.255.000] Protocol: Standard Spanning Tree Enabled: No Connector Type: 1. Execute Ping Test -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Navigation Keys: M = return to Main Menu ESC key = return to previous screen X = eXit System Management Services -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Type menu item number and press Enter or select Navigation key :
Type 1 to ping each IP address in turn.
You do not need to use this option unless your network requires a specific block size or filename.
PowerPC Firmware Version QD0123000 SLOF-SMS 1.1 (c) Copyright IBM Corp. 2007 All rights reserved. -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Advanced Setup: DHCP NET /axon@10000000000/plb5/plb4/pcix@4000004600000000/ethernet@1 1. DHCP Retries: 255 2. TFTP Blocksize: 512 3. TFTP Retries: 5 4. TFTP Filename: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Navigation Keys: M = return to Main Menu ESC key = return to previous screen X = eXit System Management Services -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Type menu item number and press Enter or select Navigation key :
At present the QS22 does not support SCSI so this option is not available.
You do not have to use this option as, by default, the current session is the active session, and QS22 does not support more than one session.
PowerPC Firmware Version QD0123000 SLOF-SMS 1.1 (c) Copyright IBM Corp. 2007 All rights reserved. -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select Console To select this console as the active console press 0 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Navigation Keys: M = return to Main Menu ESC key = return to previous screen X = eXit System Management Services -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Type menu item number and press Enter or select Navigation key :
Use this screen to select the device from which to install the operating system, the boot device and the boot device order. If you wish to install or boot from the BladeCenter unit media tray, you must first allocate it to the blade server using the Advanced Management Module.
PowerPC Firmware Version QD0123000 SLOF-SMS 1.1 (c) Copyright IBM Corp. 2007 All rights reserved. -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Multiboot 1. Select Install/Boot Device 2. Configure Boot Device Order -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Navigation Keys: M = return to Main Menu ESC key = return to previous screen X = eXit System Management Services -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Type menu item number and press Enter or select Navigation key :
To select the installation or boot device, type 1 and press Enter. The screen that appears is similar to the following:
PowerPC Firmware Version QD0123000 SLOF-SMS 1.1 (c) Copyright IBM Corp. 2007 All rights reserved. -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select Device Number Device Name . NET /axon@10000000000/plb5/plb4/pcix@4000004600000000/ethernet@1 . CDROM .../plb5/plb4/pcix@4000004600000000/usb@1/hub@1/hub@2/cdrom@3 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Navigation Keys: M = return to Main Menu ESC key = return to previous screen X = eXit System Management Services -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Type menu item number and press Enter or select Navigation key :
Only available boot devices are displayed. If you wish to boot from the CD/DVD drive in the media tray, first allocated it to the blade server using the Advanced Management Module, as otherwise, it is not shown as an available option.
PowerPC Firmware Version QD0123000 SLOF-SMS 1.1 (c) Copyright IBM Corp. 2007 All rights reserved. -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Configure Boot Device Order 1. Select 1st Boot Device 2. Select 2nd Boot Device 3. Select 3rd Boot Device 4. Select 4th Boot Device 5. Display Current Setting 6. Restore Default Setting -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Navigation Keys: M = return to Main Menu ESC key = return to previous screen X = eXit System Management Services -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Type menu item number and press Enter or select Navigation key :To set the boot device order, type the menu number according to the order you want for a particular device. For example, to choose the first boot device, type 1 and press Enter. A screen showing all the available boot devices appears:
PowerPC Firmware Version QD0123000 SLOF-SMS 1.1 (c) Copyright IBM Corp. 2007 All rights reserved. -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select Device Number Position Device Name 1. Not Specified 2. 1 NET /axon@10000000000/plb5/plb4/pcix@4000004600000000/ethernet1 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Navigation Keys: M = return to Main Menu ESC key = return to previous screen X = eXit System Management Services -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Type menu item number and press Enter or select Navigation key :The screen shows the current position in the list for the displayed boot devices. To alter the position, choose a device, type the number and press Enter. To save your selection, press M to return to the menu.
Normally the BladeCenter QS22 boots from the Temporary side and you should not change this. However, there may be occasions, for example boot failure, where you must change the setting.
PowerPC Firmware Version QD0123000 SLOF-SMS 1.1 (c) Copyright IBM Corp. 2007 All rights reserved. -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Firmware Boot Side Options Menu Firmware Boot Side for next boot: Temporary 1. Permanent 2. Temporary -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Navigation Keys: M = return to Main Menu ESC key = return to previous screen X = eXit System Management Services -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Type menu item number and press Enter or select Navigation key :
This shows the messages from the present and previous attempts to boot the blade. It also shows messages from the last occasion the blade could not boot from the Temporary side, if any.
PowerPC Firmware Version QD0123000 SLOF-SMS 1.1 (c) Copyright IBM Corp. 2007 All rights reserved. -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- View Progress Indicator History 1. Current Boot Progress Indicator 2. Previous Boot Progress Indicator 3. Previous Failover Permanent Side Boot -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Navigation Keys: M = return to Main Menu ESC key = return to previous screen X = eXit System Management Services -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Type menu item number and press Enter or select Navigation key :
The screen below shows an example of a successful previous boot:
PowerPC Firmware
Version QD0123000
SLOF-SMS 1.1 (c) Copyright IBM Corp. 2007 All rights reserved.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Progress Indicator History
Creating common NVRAM partition
C0880
Could not find SAS partition in NVRAM - created.
Adapters on 000001460ec00000
00 0800 (D) : 14e4 16a8 network [ ethernet ]
00 0900 (D) : 14e4 16a8 network [ ethernet ]
Adapters on 000001a040000000
00 0000 (B) : 1014 032c pci
Adapters on 000001a240000000
00 0000 (B) : 1014 032c pci
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Navigation Keys:
M = return to Main Menu N = Next page of list
ESC key = return to previous screen X = eXit System Management Services
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Type menu item number and press Enter or select Navigation key :
Press N to scroll through the boot history. When you have finished, press Esc to return to the menu.
The VPD on each blade server contains details about the machine type or model, serial number and the universal unique ID.
The screen is similar to the following:
PowerPC Firmware Version QD0123000 SLOF-SMS 1.1 (c) Copyright IBM Corp. 2007 All rights reserved. -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- FRU Information Machine Type and Model: 079338x Machine Serial Number: ABCDEFG Universal Unique ID: 12345678-1234-1234-1234-123456789ABC -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Navigation Keys: M = return to Main Menu ESC key = return to previous screen X = eXit System Management Services -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Select Navigation key :
When you replace a FRU details are not recorded in the VPD. You must enter them manually through SMS.
When the system firmware detects an FRU replacement part during boot the process stops to allow you to enter the machine type or model and serial number. Boot does not continue until the information is provided.
To enter new FRU information, complete the following steps:
PowerPC Firmware
Version QD0123000
SLOF-SMS 1.1 (c) Copyright IBM Corp. 2007 All rights reserved.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Enter Type Model Number
(Must be 7 characters, only A-Z, a-z, 0-9 allowed. Press Esc to skip)
Enter Type Model Number :
Type the model number according to the instructions on the screen and press Enter to continue.
PowerPC Firmware
Version QD0123000
SLOF-SMS 1.1 (c) Copyright IBM Corp. 2007 All rights reserved.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Number entered is: 1234567
Accept number?
(Enter 'y' or 'Y' to accept or 'n' or 'N' to decline)
Select Navigation key : Type y or Y and press Enter to confirm
the number.PowerPC Firmware
Version QD0123000
SLOF-SMS 1.1 (c) Copyright IBM Corp. 2007 All rights reserved.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Enter Serial Number
(Must be 7 characters, only A-Z, a-z, 0-9 allowed)
Enter Serial Number :
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------Press Enter to continue.PowerPC Firmware
Version QD0123000
SLOF-SMS 1.1 (c) Copyright IBM Corp. 2007 All rights reserved.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Number entered is: ABCDEFG
Accept number?
(Enter 'y' or 'Y' to accept or 'n' or 'N' to decline)
Select Navigation key :
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------Type y or Y and press Enter to
confirm the number.Use this option to configure or change the SAS settings if you have installed the IBM BladeCenter Boot Disk System or you installed the blade server into an IBM BladeCenter S unit.
PowerPC Firmware Version QD0123000 SLOF-SMS 1.1 (c) Copyright IBM Corp. 2007 All rights reserved. -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- SAS Settings 1. Change SAS Boot Device Address 2. Change SAS Boot Device LUN Id -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Navigation Keys: M = return to Main Menu ESC key = return to previous screen X = eXit System Management Services -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Type menu item number and press Enter or select Navigation key :
Choose 1 to set or change the SAS Boot Device Address. A screen similar to the following appears:
PowerPC Firmware Version QD0123000 SLOF-SMS 1.1 (c) Copyright IBM Corp. 2007 All rights reserved. -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Change SAS Boot Device Address Current SAS Disk Address (Default = 0) : 0 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Navigation Keys: M = return to Main Menu ESC key = return to previous screen X = eXit System Management Services -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Type SAS Address in hexadecimal and press Enter or select navigation key:
When configuring IBM BladeCenter Boot Disk System as a boot device, the SAS address can be obtained from the Storage System Profile utility. See the documentation that comes with your IBM BladeCenter Boot Disk System for more information about the Storage System Profile utility.
When configuring an IBM BladeCenter S local SAS drive as a boot device, the SAS address can obtained from the blade host firmware output.
Once you have typed the address, press Enter to add the address, then M to return to the SAS Settings menu.
Choose 2 to set or change the SAS Boot Device LUN ID. A screen similar to the following appears:
PowerPC Firmware Version QD0123000 SLOF-SMS 1.1 (c) Copyright IBM Corp. 2007 All rights reserved. -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Change SAS Boot Device LUN Id Current SAS LUN Id (Default = 0) : 0 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Navigation Keys: M = return to Main Menu ESC key = return to previous screen X = eXit System Management Services -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Type new LUN Id in hexadecimal and press Enter or select navigation key:
When configuring IBM BladeCenter Boot Disk System as a boot device, the LUN Id can be obtained from the Storage System Profile utility. See the documentation that comes with your IBM BladeCenter Boot Disk System for more information about the Storage System Profile utility.
When configuring an IBM BladeCenter S local SAS drive as a boot device, use 0 as the LUN Id.
If you need help, service, or technical assistance or just want more information about IBM products, you will find a wide variety of sources available from IBM to assist you. This appendix contains information about where to go for additional information about IBM and IBM products, what to do if you experience a problem with your BladeCenter product or optional device, and whom to call for service, if it is necessary.
Before you call, make sure that you have taken these steps to try to solve the problem yourself:
You can solve many problems without outside assistance by following the troubleshooting procedures that IBM provides in the online help or in the documentation that is provided with your IBM product. The documentation that comes with BladeCenter systems also describes the diagnostic tests that you can perform. Most BladeCenter systems, operating systems, and programs come with documentation that contains troubleshooting procedures and explanations of error messages and error codes. If you suspect a software problem, see the documentation for the software.
Information about your IBM BladeCenter system and preinstalled software, if any, or optional device is available in the documentation that comes with the product. That documentation can include printed documents, online documents, readme files, and help files. See the troubleshooting information in your system documentation for instructions for using the diagnostic programs. The troubleshooting information or the diagnostic programs might tell you that you need additional or updated device drivers or other software. IBM maintains pages on the World Wide Web where you can get the latest technical information and download device drivers and updates. To access these pages, go to http://www.ibm.com/systems/bladecenter/support/ and follow the instructions. Also, some documents are available through the IBM Publications Center at http://www.ibm.com/shop/publications/order/.
On the World Wide Web, the IBM Web site has up-to-date information about IBM systems, optional devices, services, and support. The address for IBM BladeCenter information is http://www.ibm.com/systems/bladecenter/.
You can find service information for IBM systems and optional devices at http://www.ibm.com/systems/support/.
Through IBM Support Line, you can get telephone assistance, for a fee, with usage, configuration, and software problems with BladeCenter products. For information about which products are supported by Support Line in your country or region, see http://www.ibm.com/services/sl/products/.
For more information about Support Line and other IBM services, see http://www.ibm.com/services/us/, or see http://www.ibm.com/planetwide/ for support telephone numbers. In the U.S. and Canada, call 1-800-IBM-SERV (1-800-426-7378).
You can receive hardware service through IBM Services or through your IBM reseller, if your reseller is authorized by IBM to provide warranty service. See http://www.ibm.com/planetwide/ for support telephone numbers, or in the U.S. and Canada, call 1-800-IBM-SERV (1-800-426-7378).
In the U.S. and Canada, hardware service and support is available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. In the U.K., these services are available Monday through Friday, from 9 a.m. to 6 p.m.
This information was developed for products and services offered in the U.S.A.
IBM may not offer the products, services, or features discussed in this document in other countries. Consult your local IBM representative for information on the products and services currently available in your area. Any reference to an IBM product, program, or service is not intended to state or imply that only that IBM product, program, or service may be used. Any functionally equivalent product, program, or service that does not infringe any IBM intellectual property right may be used instead. However, it is the user's responsibility to evaluate and verify the operation of any non-IBM product, program, or service.
IBM may have patents or pending patent applications covering subject matter described in this document. The furnishing of this document does not give you any license to these patents. You can send license inquiries, in writing, to:
INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS MACHINES CORPORATION PROVIDES THIS PUBLICATION "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF NON-INFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Some states do not allow disclaimer of express or implied warranties in certain transactions, therefore, this statement may not apply to you.
This information could include technical inaccuracies or typographical errors. Changes are periodically made to the information herein; these changes will be incorporated in new editions of the publication. IBM may make improvements and/or changes in the product(s) and/or the program(s) described in this publication at any time without notice.
Any references in this information to non-IBM Web sites are provided for convenience only and do not in any manner serve as an endorsement of those Web sites. The materials at those Web sites are not part of the materials for this IBM product, and use of those Web sites is at your own risk.
IBM may use or distribute any of the information you supply in any way it believes appropriate without incurring any obligation to you.
IBM, the IBM logo, and ibm.com are trademarks or registered trademarks of International Business Machines Corporation in the United States, other countries, or both. If these and other IBM trademarked terms are marked on their first occurrence in this information with a trademark symbol (® or ™), these symbols indicate U.S. registered or common law trademarks owned by IBM at the time this information was published. Such trademarks may also be registered or common law trademarks in other countries. A current list of IBM trademarks is available on the Web at "Copyright and trademark information" at http://www.ibm.com/legal/copytrade.shtml.
Cell Broadband Engine is a trademark of Sony Computer Entertainment, Inc., in the United States, other countries, or both and is used under license therefrom.
Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds in the United States, other countries, or both.
Other company, product, or service names may be trademarks or service marks of others.
Processor speed indicates the internal clock speed of the microprocessor; other factors also affect application performance.
CD or DVD drive speed is the variable read rate. Actual speeds vary and are often less than the possible maximum.
When referring to processor storage, real and virtual storage, or channel volume, KB stands for 1024 bytes, MB stands for 1 048 576 bytes, and GB stands for 1 073 741 824 bytes.
When referring to hard disk drive capacity or communications volume, MB stands for 1 000 000 bytes, and GB stands for 1 000 000 000 bytes. Total user-accessible capacity can vary depending on operating environments.
Maximum internal hard disk drive capacities assume the replacement of any standard hard disk drives and population of all hard disk drive bays with the largest currently supported drives that are available from IBM.
Maximum memory might require replacement of the standard memory with an optional memory module.
IBM makes no representation or warranties regarding non-IBM products and services that are ServerProven®, including but not limited to the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. These products are offered and warranted solely by third parties.
IBM makes no representations or warranties with respect to non-IBM products. Support (if any) for the non-IBM products is provided by the third party, not IBM.
Some software might differ from its retail version (if available) and might not include user manuals or all program functionality.
This unit must be recycled or discarded according to applicable local and national regulations. IBM encourages owners of information technology (IT) equipment to responsibly recycle their equipment when it is no longer needed. IBM offers a variety of product return programs and services in several countries to assist equipment owners in recycling their IT products. Information on IBM product recycling offerings can be found on IBM's Internet site at http://www.ibm.com/ibm/environment/products/index.shtml.
Esta unidad debe reciclarse o desecharse de acuerdo con lo establecido en la normativa nacional o local aplicable. IBM recomienda a los propietarios de equipos de tecnología de la información (TI) que reciclen responsablemente sus equipos cuando éstos ya no les sean útiles. IBM dispone de una serie de programas y servicios de devolución de productos en varios países, a fin de ayudar a los propietarios de equipos a reciclar sus productos de TI. Se puede encontrar información sobre las ofertas de reciclado de productos de IBM en el sitio web de IBM http://www.ibm.com/ibm/environment/products/index.shtml.
Notice: This mark applies only to countries within the European Union (EU).
Batteries or packaging for batteries are labeled in accordance with European Directive 2006/66/EC concerning batteries and accumulators and waste batteries and accumulators. The Directive determines the framework for the return and recycling of used batteries and accumulators as applicable throughout the European Union. This label is applied to various batteries to indicate that the battery is not to be thrown away, but rather reclaimed upon end of life per the Directive.
In accordance with the European Directive 2006/66/EC, batteries and accumulators are labeled to indicate that they are to be collected separately and recycled at end of life. The label on the battery may also include a chemical symbol for the metal concerned in the battery (Pb for lead, Hg for mercury and Cd for cadmium). Users of batteries and accumulators must not dispose of batteries and accumulators as unsorted municipal waste, but use the collection framework available to customers for the return, recycling and treatment of batteries and accumulators. Customer participation is important to minimize any potential effects of batteries and accumulators on the environment and human health due to the potential presence of hazardous substances.
The retail price of batteries, accumulators and power cells includes the cost of the environmental management of their waste. For proper collection and treatment, contact your local IBM representative.

Remarque : Cette marque s'applique uniquement aux pays de l'Union Européenne et à la Norvège.
L'etiquette du système respecte la Directive européenne 2002/96/EC en matière de Déchets des Equipements Electriques et Electroniques (DEEE), qui détermine les dispositions de retour et de recyclage applicables aux systèmes utilisés à travers l'Union européenne. Conformément à la directive, ladite étiquette précise que le produit sur lequel elle est apposée ne doit pas être jeté mais être récupéré en fin de vie.
In accordance with the European WEEE Directive, electrical and electronic equipment (EEE) is to be collected separately and to be reused, recycled, or recovered at end of life. Users of EEE with the WEEE marking per Annex IV of the WEEE Directive, as shown above, must not dispose of end of life EEE as unsorted municipal waste, but use the collection framework available to customers for the return, recycling, and recovery of WEEE. Customer participation is important to minimize any potential effects of EEE on the environment and human health due to the potential presence of hazardous substances in EEE. For proper collection and treatment, contact your local IBM representative.
This product may contain a sealed lead acid, nickel cadmium, nickel metal hydride, lithium, or lithium ion battery. Consult your user manual or service manual for specific battery information. The battery must be recycled or disposed of properly. Recycling facilities may not be available in your area. For information on disposal of batteries outside the United States, go to http://www.ibm.com/ibm/environment/products/index.shtml or contact your local waste disposal facility.
In the United States, IBM has established a return process for reuse, recycling, or proper disposal of used IBM sealed lead acid, nickel cadmium, nickel metal hydride, and battery packs from IBM equipment. For information on proper disposal of these batteries, contact IBM at 1-800-426-4333. Have the IBM part number listed on the battery available prior to your call.
For Taiwan: Please recycle batteries.
For the European Union:

Notice: This mark applies only to countries within the European Union (EU).
Batteries or packaging for batteries are labeled in accordance with European Directive 2006/66/EC concerning batteries and accumulators and waste batteries and accumulators. The Directive determines the framework for the return and recycling of used batteries and accumulators as applicable throughout the European Union. This label is applied to various batteries to indicate that the battery is not to be thrown away, but rather reclaimed upon end of life per this Directive.
Les batteries ou emballages pour batteries sont étiquetés conformément aux directives européennes 2006/66/EC, norme relative aux batteries et accumulateurs en usage et aux batteries et accumulateurs usés. Les directives déterminent la marche à suivre en vigueur dans l'Union Européenne pour le retour et le recyclage des batteries et accumulateurs usés. Cette étiquette est appliquée sur diverses batteries pour indiquer que la batterie ne doit pas être mise au rebut mais plutôt récupérée en fin de cycle de vie selon cette norme.

In accordance with the European Directive 2006/66/EC, batteries and accumulators are labeled to indicate that they are to be collected separately and recycled at end of life. The label on the battery may also include a chemical symbol for the metal concerned in the battery (Pb for lead, Hg for mercury, and Cd for cadmium). Users of batteries and accumulators must not dispose of batteries and accumulators as unsorted municipal waste, but use the collection framework available to customers for the return, recycling, and treatment of batteries and accumulators. Customer participation is important to minimize any potential effects of batteries and accumulators on the environment and human health due to the potential presence of hazardous substances. For proper collection and treatment, contact your local IBM representative.
This notice is provided in accordance with Royal Decree 106/2008 of Spain: The retail price of batteries, accumulators, and power cells includes the cost of the environmental management of their waste.
For California:
Perchlorate material - special handling may apply. See http://www.dtsc.ca.gov/hazardouswaste/perchlorate/.
The foregoing notice is provided in accordance with California Code of Regulations Title 22, Division 4.5 Chapter 33. Best Management Practices for Perchlorate Materials. This product/part may include a lithium manganese dioxide battery which contains a perchlorate substance.
Note: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference, in which case the user will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
Properly shielded and grounded cables and connectors must be used in order to meet FCC emission limits. IBM is not responsible for any radio or television interference caused by using other than recommended cables and connectors or by unauthorized changes or modifications to this equipment. Unauthorized changes or modifications could void the user's authority to operate the equipment.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
This Class A digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe A est conforme à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
Notice to Customers
This apparatus is approved under approval number NS/G/1234/J/100003 for indirect connection to public telecommunication systems in the United Kingdom.
Dieses Produkt entspricht den Schutzanforderungen der EU-Richtlinie 2004/108/EG zur Angleichung der Rechtsvorschriften über die elektromagnetische Verträglichkeit in den EU-Mitgliedsstaaten und hält die Grenzwerte der EN 55022 Klasse A ein.
Um dieses sicherzustellen, sind die Geräte wie in den Handbüchern beschrieben zu installieren und zu betreiben. Des Weiteren dürfen auch nur von der IBM empfohlene Kabel angeschlossen werden. IBM übernimmt keine Verantwortung für die Einhaltung der Schutzanforderungen, wenn das Produkt ohne Zustimmung der IBM verändert bzw. wenn Erweiterungskomponenten von Fremdherstellern ohne Empfehlung der IBM gesteckt/eingebaut werden.
EN 55022 Klasse A Geräte müssen mit folgendem Warnhinweis versehen werden:
"Warnung: Dieses ist eine Einrichtung der Klasse A. Diese Einrichtung kann im Wohnbereich Funk-Störungen verursachen; in diesem Fall kann vom Betreiber verlangt werden, angemessene Maßnahmen zu ergreifen und dafür aufzukommen."
Dieses Produkt entspricht dem "Gesetz über die elektromagnetische Verträglichkeit von Geräten (EMVG)". Dies ist die Umsetzung der EU-Richtlinie 2004/108/EG in der Bundesrepublik Deutschland.
Dieses Gerät ist berechtigt, in Übereinstimmung mit dem Deutschen EMVG das EG-Konformitätszeichen - CE - zu führen.
Verantwortlich für die Konformitätserklärung des EMVG ist die IBM Deutschland GmbH, 70548 Stuttgart.
Generelle Informationen:
Das Gerät erfüllt die Schutzanforderungen nach EN 55024 und EN 55022 Klasse A.
This product is in conformity with the protection requirements of EU Council Directive 2004/108/EC on the approximation of the laws of the Member States relating to electromagnetic compatibility. IBM cannot accept responsibility for any failure to satisfy the protection requirements resulting from a nonrecommended modification of the product, including the fitting of non-IBM option cards.
This product has been tested and found to comply with the limits for Class A Information Technology Equipment according to CISPR 22/European Standard EN 55022. The limits for Class A equipment were derived for commercial and industrial environments to provide reasonable protection against interference with licensed communication equipment.
European Community contact:



